
- Read more about Super-Resolution in Compressive Coded Imaging Systems via l2 − l1 − l2 Minimization Under a Deep Learning Approach
- Log in to post comments
In most imaging applications the spatial resolution is a concern of the systems, but increasing the resolution of the sensor increases substantially the implementation cost. One option with lower cost is the use of spatial light modulators, which allows improving the reconstructed image resolution by including a high-resolution codification.
- Categories:
 142 Views
142 Views
- Read more about Tensor Dictionary Learning with representation quantization for Remote Sensing Observation Compression
- Log in to post comments
Nowadays, multidimensional data structures, known as tensors, are widely used in many applications like earth observation from remote sensing image sequences. However, the increasing spatial, spectral and temporal resolution of the acquired images, introduces considerable challenges in terms of data storage and transfer, making critical the necessity of an efficient compression system for high dimensional data. In this paper, we propose a tensor-based compression algorithm that retains the structure of the data and achieves a high compression ratio.
dcc_aidini.pdf
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about Spatial-Temporal Fusion Convolutional Neural Network for Compressed Video enhancement in HEVC
- Log in to post comments
DCC-2020.ppt
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Compressive Classification via Deep Learning using Single-pixel Measurements
- Log in to post comments
Single-pixel camera (SPC) captures encoded projections of the scene in a unique detector such that the number of compressive projections is lower than the size of the image. Traditionally, classification is not performed in the compressive domain because it is necessary to recover the underlying image before to classification. Based on the success of Deep Learning (DL) in classification approaches, this paper proposes to classify images using compressive measurements of SPC.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views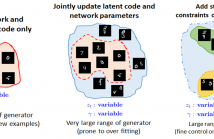
- Read more about GENERATIVE MODELS FOR LOW-RANK VIDEO REPRESENTATION AND RECONSTRUCTION FROM COMPRESSIVE MEASUREMENTS
- Log in to post comments
Generative models have recently received considerable attention in the field of compressive sensing. If an image belongs to the range of a pretrained generative network, we can recover it from its compressive measurements by estimating the underlying compact latent code. In practice, all the pretrained generators have certain range beyond which they fail to generate reliably. Recent researches show that convolutional generative structures are biased to generate natural images.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Learning Product Codebooks using Vector-Quantized Autoencoders for Image Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
SIP2019.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about 3D Shape Retrieval Through Multilayer RBF Neural Network
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
3D object retrieval involves more efforts mainly because major computer vision features are designed for 2D images, which is rarely applicable for 3D models. In this paper, we propose to retrieve the 3D models based on the implicit parameters learned from the radial base functions that represent the 3D objects. The radial base functions are learned from the RBF neural network. As deep neural networks can represent the data that is not linearly separable, we apply multiple layers' neural network to train the radial base functions.
icip3549.pdf
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Dual reverse attention networks for person re-identification
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we enhance feature representation ability of person re-identification (Re-ID) by learning invariances to hard examples. Unlike previous works of hard examples mining and generating in image level, we propose a dual reverse attention network (DRANet) to generate hard examples in the convolutional feature space. Specifically, we use a classification branch of attention mechanism to model that ‘what’ in channel and ‘where’ in spatial dimensions are informative in the feature maps.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
This paper proposes an approach to automatically categorize the social interactions of a user wearing a photo-camera (2fpm), by relying solely on what the camera is seeing. The problem is challenging due to the overwhelming complexity of social life and the extreme intra-class variability of social interactions captured under unconstrained conditions. We adopt the formalization proposed in Bugental’s social theory, that groups human relations into five social domains with related categories.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about TAKING ME TO THE CORRECT PLACE: VISION-BASED LOCALIZATION FOR AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Vehicle localization is a critical component for autonomous driving, which estimates the position and orientation of vehicles. To achieve the goal of quick and accurate localization, we develop a system that can dynamically switch the features applied for localization. Specifically, we develop a feature based on convolutional neural network targeting at accurate matching, which proves high rotation invariant property that can help to overcome the relatively large error when vehicles turning at corners.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views