- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about PROPER GUIDANCE IMAGE GENERATION BASED ON SALIENCY FACTOR FOR BETTER TRANSMISSION REFINEMENT IN IMAGE DEHAZING
- Log in to post comments
Guided image filter is one of the most commonly used ways to refine transmission maps. However, since this filter transfers the structures of the guidance image to the filtering output, when the guidance image is the input image itself, even small textures in the input image will cause the change of transmission, which is obviously contrary to the principle that transmission changes only when scene depth changes. In this paper, saliency detection, which simulates the way human eyes work, is introduced into haze removal to tackle the above issue.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Image Reflection Removal Using The Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network
- Log in to post comments
Imaging through a semi-transparent material such as glass often suffers from the reflection problem, which degrades the image quality. Reflection removal is a challenging task since it is severely ill-posed. Traditional methods, while all require long computation time on minimizing different objective functions with huge matrices, do not necessarily give satisfactory performance. In this paper, we propose a novel deep-learning based method to allow fast removal of reflection.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about MULTI-SCALE SPATIAL-TEMPORAL NETWORK FOR PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
last_version1.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are nowadays achieving significant leaps in different pattern recognition tasks including action recognition. Current CNNs are increasingly deeper, data-hungrier and this makes their success tributary of the abundance of labeled training data. CNNs also rely on max/average pooling which reduces dimensionality of output layers and hence attenuates their sensitivity to the availability of labeled data.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about USING DEEP CROSS MODAL HASHING AND ERROR CORRECTING CODES FOR IMPROVING THE EFFICIENCY OF ATTRIBUTE GUIDED FACIAL IMAGE RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
With benefits of fast query speed and low storage cost,hashing-based image retrieval approaches have garnered considerable attention from the research community. In this pa-per, we propose a novel Error-Corrected Deep Cross Modal Hashing (CMH-ECC) method which uses a bitmap specifying the presence of certain facial attributes as an input query to retrieve relevant face images from the database.
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views
- Read more about FAST IMAGE MATCHING BASED ON FOURIER-MELLIN PHASE CORRELATION FOR TAG-LESS IDENTIFICATION OF MASS-PRODUCED PARTS
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a fast technique for matching a query image to numerous database images under geometric variations in rotation, scale, and translation. Our proposed method extracts the Fourier-Mellin phase features from the images for invariant matching. The online matching process in our method is fast because it directly determines identification based on the correlation value between those features without the geometric alignment.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views- Read more about Model Corrected Low Rank Ptychography
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we introduce a novel algorithmic framework for sub-diffractive super-resolution imaging of dynamic, time varying targets. We extend recent works in low rank Fourier ptychographic imaging, to incorporate model-correction schemes, which correct for errors propagated due to inaccuracies in fitting an exact low rank model to the target video acquired. Through our algorithm, we are able to demonstrate superior reconstruction quality of video from phaseless Fourier ptychographic measurements, at low sample complexities, as compared to conventional ptychographic setups.
poster_icip.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views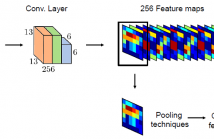
- Read more about PYRAMID POOLING OF CONVOLTIONAL FEATURE MAPS FOR IMAGE RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel method for content-based image retrieval based on the features extracted from the convolutional layers of the deep neural network architecture. Some of the popular approaches form the feature vectors from the fully connected layers of the convolutional neural networks or directly concatenate the features from the convolutional layers. However, the main problem with the use of feature vectors from fully connected layers is that the spatial information about the objects is lost. This motivated us to use the features from the convolutional layer.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about HADAMARD CODED DISCRETE CROSS MODAL HASHING
- Log in to post comments
Cross-modal retrieval is a hot topic in the fields of machine learning and media retrieval, making it possible to relate different types of media, such as image, text, and audio. A powerful method for the cross-modal retrieval, discrete cross-modal hashing (DCH), has recently been proposed. The DCH can encode different types of media feature vectors to binary codes. When stored in a database, the binary code makes searches efficient because the Hamming distance between the corresponding sections of two binary codes can be computed via a specialized CPU operation.
ICIPposter.pdf
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views