
- Read more about ADVERSARIAL INPAINTING OF MEDICAL IMAGE MODALITIES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
- Read more about BI-RADS classification of breat cancer: a new pre-processing pipeline for deep models training
- Log in to post comments
One of the main difficulties in the use of deep learning strategies in medical contexts is the training set size. While these methods need large annotated training sets, this data is costly to obtain in medical contexts and suffers from intra and iter-subject variability.
In the present work, two new pre-processing techniques are introduced to improve a classifier performance. First, data augmentation based on co-registration is suggested. Then, multi-scale enhancement based on Difference of Gaussians is proposed.
Poster_A0.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Deep Residual Learning for Model-Based Iterative CT Reconstruction using Plug-and-Play Framework
- Log in to post comments
Model-Based Iterative Reconstruction (MBIR) has shown promising results in clinical studies as they allow significant
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views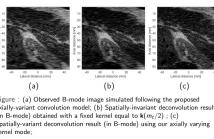
- Read more about Restoration of ultrasound images using spatially-variant kernel deconvolution
- Log in to post comments
Most of the existing ultrasound image restoration methods consider a spatially-invariant point-spread function (PSF) model and circulant boundary conditions. While computationally efficient, this model is not realistic and severely limits the quality of reconstructed images. In this work, we address ultrasound image restoration under the hypothesis of vertical variation of the PSF. To regularize the solution, we use the classical elastic net constraint.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about AN ATTENUATION ADAPTED PULSE COMPRESSION TECHNIQUE TO ENHANCE THE BANDWIDTH AND THE RESOLUTION USING ULTRAFAST ULTRASOUND IMAGING
- Log in to post comments
Recent studies suggest that Resolution Enhancement Compression (REC) can provide significant improvements in terms of imaging quality over Classical Pulsed (CP) ultrasonic imaging techniques, by employing frequency and amplitude modulated transmitted signals. However the performance of coded excitations methods degrades drastically deeper into the tissue where the attenuation effects become more significant. In this work, a technique that allows overcoming the effects of attenuation on REC imaging is proposed (REC-Opt).
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about SEGMENTATION AND TRACKING OF INFERIOR VENA CAVA IN ULTRASOUND IMAGES USING A NOVEL POLAR ACTIVE CONTOUR ALGORITHM
- Log in to post comments
Medical research suggests that the area of the IVC and its temporal variation imaged by bedside ultrasound is useful in guiding resuscitation of the critically-ill. Unfortunately, gaps in the vessel wall and intraliminal artifact represents a challenge for both manual and existing algorithm-based segmentation techniques.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views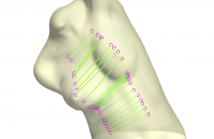
- Read more about 3D SHAPE ASYMMETRY ANALYSIS USING CORRESPONDENCE BETWEEN PARTIAL GEODESIC CURVES
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Analyzing the asymmetry of anatomical shapes is one of the cornerstones of efficient computerized diagnosis. In the application of scoliotic trunk analysis, one major challenge is the high variability and complexity of deformations due to the pathology itself, and to changes of body poses, for instance, torsos acquired in lateral bending poses for surgical planning. In this paper, we present a novel and fully automatic approach to analyzing the asymmetry of deformable trunk shapes.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about LESION DETECTION USING T1-WEIGHTED MRI: A NEW APPROACH BASED ON FUNCTIONAL CORTICAL ROIS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about COMPARISON OF OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS IN CNN-BASED PROSTATE MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGE SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
We investigate the impacts of objective functions on the performance of deep-learning-based prostate magnetic resonance image segmentation. To this end, we first develop a baseline convolutional neural network (BCNN) for the prostate image segmentation, which consists of encoding, bridge, decoding, and classification modules. In the BCNN, we use 3D convolutional layers to consider volumetric information. Also, we adopt the residual feature forwarding and intermediate feature propagation techniques to make the BCNN reliably trainable for various objective functions.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views