- Read more about Accurate colon segmentation using 2D convolutional neural networks with 3D contextual information
- Log in to post comments
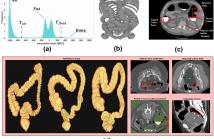
This study introduces an innovative framework for accurate colon segmentation in abdomen CT scans, addressing the unique challenges of this task. Our architecture enhances well-established 2D segmentation models by incorporating 3D contextual information through a novel method that generates an attention map for a given slice by considering its neighboring slices. This approach achieves effective colon segmentation without complex 3D convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks by combining 2D CNNs.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Unrolled Projected Gradient Algorithm for Stain Separation in Digital Histopathological Images
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a novel optimization approach for stain separation in digital histopathological images. Our stain separation cost function incorporates a smooth total variation regularization and is minimized by using a projected gradient algorithm. To enhance computational efficiency and enable supervised learning of the hyperparameters, we further unroll our algorithm into a neural network. The unrolled architecture is not only more efficient for solving the stain separation problem, but also allows to design a highly interpretable and flexible method.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about SCORE-BASED DIFFUSION MODELS FOR PHOTOACOUSTIC TOMOGRAPHY IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION
- Log in to post comments
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is a rapidly-evolving medical imaging modality that combines optical absorption contrast with ultrasound imaging depth. One challenge in PAT is image reconstruction with inadequate acoustic signals due to limited sensor coverage or due to the density of the transducer array. Such cases call for solving an ill-posed inverse reconstruction problem. In this work, we use score-based diffusion models to solve the inverse problem of reconstructing an image from limited PAT measurements.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views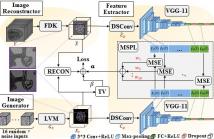
- Read more about STABLE OPTIMIZATION FOR LARGE VISION MODEL BASED DEEP IMAGE PRIOR IN CONE-BEAM CT RECONSTRUCTION
- Log in to post comments
Large Vision Model (LVM) has recently demonstrated great potential for medical imaging tasks, potentially enabling image enhancement for sparse-view Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), despite requiring a substantial amount of data for training. Meanwhile, Deep Image Prior (DIP) effectively guides an untrained neural network to generate high-quality CBCT images without any training data. How- ever, the original DIP method relies on a well-defined forward model and a large-capacity backbone network, which is no- toriously difficult to converge.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Physics-Guided Deep Scatter Estimation by Weakly Supervision for Quantitative SPECT
- Log in to post comments
Accurate scatter estimation is important in quantitative SPECT for improving image contrast and accuracy. With a large number of photon histories, Monte-Carlo (MC) simulation can yield accurate scatter estimation, but is computationally expensive. Recent deep learning-based approaches can yield accurate scatter estimates quickly, yet full MC simulation is still required to generate scatter estimates as ground truth labels for all training data.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about ViTASD: Robust Vision Transformer Baselines for Autism Spectrum Disorder Facial Diagnosis
- Log in to post comments
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder with very high prevalence around the world. Research progress in the field of ASD facial analysis in pediatric patients has been hindered due to a lack of well-established baselines. In this paper, we propose the use of the Vision Transformer (ViT) for the computational analysis of pediatric ASD. The presented model, known as ViTASD, distills knowledge from large facial expression datasets and offers model structure transferability.
370_Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 88 Views
88 Views
A common approach for enabling remote radiologists to view medical images is to provide them with secure access to a cloud instance using a web-based application. Such solutions must transcode input images or videos to low latency, lossless bit streams and make them available to remote users. The heart of the solution is the highly efficient, low-latency, and hardware-agnostic compression scheme. This poster surveys potential codecs for the low-latency, lossless compression of 16-bit RAW monochrome medical images and compares the compression ratio and encode time for each.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about A Minimally Supervised Approach for Medical Image Quality Assessment in Domain Shift Settings
- Log in to post comments
Accurate disease diagnosis requires objective assessment of clinical image quality. Automated image quality assessment (IQA) could enhance screening and diagnosis workflows. However, development of generalizable quality assessment tools requires large labeled clinical image datasets from different sites. Obtaining these datasets is often infeasible; and quality indicators may vary with acquisition settings due to domain shift. We introduce a minimally-supervised
8754-2.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about UNSUPERVISED DEEP LEARNING NETWORK FOR DEFORMABLE FUNDUS IMAGE REGISTRATION
- Log in to post comments
In ophthalmology and vision science applications, the process of registering a pair of fundus images, captured at different scales and viewing angles, is of paramount importance to support the diagnosis of diseases and routine eye examinations. Aiming at addressing the retina registration problem from the Deep Learning perspective, in this paper we introduce an end-to-end framework capable of learning the registration task in a fully unsupervised way.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views