- Read more about ScribbeDiff
- Log in to post comments
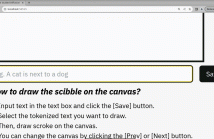
Recent advancements in text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable success, yet they often struggle to fully capture the user's intent.
Existing approaches using textual inputs combined with bounding boxes or region masks fall short in providing precise spatial guidance, often leading to misaligned or unintended object orientation.
To address these limitations, we propose Scribble-Guided Diffusion (ScribbleDiff), a training-free approach that utilizes simple user-provided scribbles as visual prompts to guide image generation.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about FreeTalker: Controllable Speech and Text-Driven Gesture Generation Based on Diffusion Models for Enhanced Speaker Naturalness
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Current talking avatars mostly generate co-speech gestures based on audio and text of the utterance, without considering the non-speaking motion of the speaker. Furthermore, previous works on co-speech gesture generation have designed network structures based on individual gesture datasets, which results in limited data volume, compromised generalizability, and restricted speaker movements.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Txt2Vid-Web: Web-based, Text-to-Video, Video Conferencing Pipeline
- Log in to post comments
Video conferencing tools have seen a significant increase in usage in the past few years but they still consume a significant bandwidth of ~100 Kbps to a few Mbps. In this work, we present Txt2Vid-Web: a practical, web-based, low bandwidth, video conferencing platform building upon the Txt2Vid work [1].
- Categories:
 222 Views
222 Views
- Read more about Assessment of Bipolar Disorder Using Heterogeneous Data of Smartphone-based Digital Phenotyping
- Log in to post comments
Bipolar Disorder (BD) is one of the most common mental illness. Using rating scales for assessment is one of the approaches for diagnosing and tracking BD patients. However, the requirement for manpower and time is heavy in the process of evaluation. In order to reduce the cost of social and medical resources, this study collects the user’s data by the App on smartphones, consisting of location data, self-report scales, daily mood, sleeping time and records of multi-media which are heterogeneous digital phenotyping data, to build a database.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Framework for promoting social interaction and physical activity in elderly people using gamification and fuzzy logic strategy
- Log in to post comments
Elderly people commonly face health problems related to their sedentary life. Thus, their physical strength, mental capability, and motor skills are decreasing. Moreover, overweight and physical problems are becoming a serious health problem around the world. On the other hand, they suffer from the social isolation that directly affects their physical and mental health. Gamification for elderly people emerges to motivate them to exercise and socialize with their peers, through social interaction on mobile devices.
- Categories:
 217 Views
217 Views
- Read more about DEPTH FROM GAZE
- Log in to post comments
Eye trackers are found on various electronic devices. In this paper, we propose to exploit the gaze information acquired by an eye tracker for depth estimation. The data collected from the eye tracker in a fixation interval are used to estimate the depth of a gazed object. The proposed method can be used to construct a sparse depth map of an augmented reality space. The resulting depth map can be applied to, for example, controlling the visual information displayed to the viewer.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about Multimodal Signal Processing and Learning Aspects of Human-Robot Interaction for an Assistive Bathing Robot
- Log in to post comments
We explore new aspects of assistive living on smart human-robot interaction (HRI) that involve automatic recognition and online validation of speech and gestures in a natural interface, providing social features for HRI. We introduce a whole framework and resources of a real-life scenario for elderly subjects supported by an assistive bathing robot, addressing health and hygiene care issues.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Affect Recognition from Lip Articulations
- Log in to post comments
Lips deliver visually active clues for speech articulation. Affective states define how humans articulate speech; hence, they also change articulation of lip motion. In this paper, we investigate effect of phonetic classes for affect recognition from lip articulations. The affect recognition problem is formalized in discrete activation, valence and dominance attributes. We use the symmetric Kullback-Leibler divergence (KLD) to rate phonetic classes with larger discrimination across different affective states. We perform experimental evaluations using the IEMOCAP database.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about Use of Affect Based Interaction Classification for Continuous Emotion Tracking
- Log in to post comments
Natural and affective handshakes of two participants define the course of dyadic interaction. Affective states of the participants are expected to be correlated with the nature of the dyadic interaction. In this paper, we extract two classes of the dyadic interaction based on temporal clustering of affective states. We use the k-means temporal clustering to define the interaction classes, and utilize support vector machine based classifier to estimate the interaction class types from multimodal, speech and motion, features.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Agreement and Disagreement Classification of Dyadic Interactions Using Vocal and Gestural Cues
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views