
The IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP) is a flagship conference of the IEEE Signal Processing Society. GlobalSIP'15 will be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, December 14-16, 2015. The conference will focus on signal and information processing with an emphasis on up-and-coming signal processing themes. The conference will feature world-class speakers, tutorials, exhibits, and sessions consisting of poster or oral presentations. Outstanding papers will be selected for Best Paper Awards or Best Student Paper Awards; a paper is eligible for a best student paper award if the first author of the paper is a student. IEEE Signal Processing Society and National Science Foundation will provide travel grants to eligible students.
- Read more about DELAY-LESS FREQUENCY DOMAIN PACKET-LOSS CONCEALMENT FOR TONAL AUDIO SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about Decentralized Coordinated Beamforming for Weighted Sum Energy Efficiency Maximization in Multi-Cell MISO Downlink
- Log in to post comments
We study energy-efficient decentralized coordinated beamforming in multi-cell multiuser multiple-input single-output system. The problem of interest is to maximize the weighted sum energy efficiency subject to user-specific quality of service constraints. The original problem is iteratively approximated as a convex program according to successive convex approximation (SCA) principle. The convex problem at each iteration is then formulated as a general global
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Better than l0 Recovery via Blind Identification
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a novel approach to multiple measurement vector (MMV) compressed sensing. We show that by exploiting the statistical properties of the sources, we can do better than previously derived lower bounds in this context. We show that in the MMV case, we can identify the active sources with fewer sensors than sources. We first develop a general framework for recovering the sparsity profile of the sources by combining ideas from compressed sensing with blind identification methods.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
This presentation describes the bandwidth extension (BWE) method developed for the AMR-WB interoperable (AMR-WB IO) modes of the 3GPP EVS codec. The low-band signal (0-6.4 kHz) is coded using an enhanced version of ACELP as in AMR-WB and post-processed; the high-band (above 6.4 kHz) in contrast to AMR-WB is represented with a new BWE method. The decoded low-band excitation is adaptively extended to high frequencies and filtered in the DCT domain. The extended excitation is scaled by subframe gains and shaped by a weighted LPC synthesis filter.
- Categories:
 200 Views
200 Views
- Read more about A Novel Frequency Domain BWE with Relaxed Synchronization and Associated BWE Switching
- Log in to post comments
This presentation describes a novel frequency domain bandwidth extension (BWE) scheme with relaxed synchronization, optimized for coding inactive and music/mixed content signals. The algorithm achieves high subjective quality at low and medium bitrates and it has a low algorithmic delay. The algorithm is part of the 3GPP Enhanced Voice Services (EVS) codec. In addition to the presented algorithm, the EVS codec employs also a time domain BWE scheme optimized for active speech coding.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Audio Bandwidth Detection in the EVS Codec
- Log in to post comments
Speech and audio codecs are usually designed such that they encode all the frequency bands of the input signal spectrum. If the higher bands do not contain any perceptually meaningful content, these codecs often do not work optimally as they assign part of the available bit budget to encode these bands. In this paper we describe a bandwidth detection algorithm that determines the effective audio bandwidth of the input signal.
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views- Read more about Coding Performance for Signal Dependent Channels in Visible Light Communication System
- Log in to post comments
GlobalSIP.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views- Read more about Model-based Color Natural Stochastic Textures Processing and Classification
- Log in to post comments
gs15_pres.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views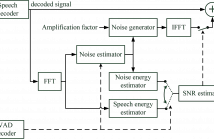
- Read more about A COMFORT NOISE ADDITION POST-PROCESSOR FOR ENHANCING LOW BIT-RATE SPEECH CODING IN NOISY ENVIRONMENTS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about Data rate maximization based power allocation for OFDM System in a High-Speed Train Environment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views