
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about MUSeed: A Mobile Image Analysis Application for Plant Seed Morphometry
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about EXTENDED CONJUGATE POLAR FOURIER TRANSFORM IN CONVOLUTION NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes an extended conjugate polar Fourier transform (ECPFT), to design iterated radial filter bank (RFB) and directional filter bank (DFB) convenient for accurate multiscale and multidirectional decomposition in discretization over a convolution network. With conjugated symmetric form, ECPFT would convert complex directional wavelets in original spatial domain to real ones in the inverse Fourier domain of ECPFT.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views- Read more about Perceptual metric for color transfer methods
- Log in to post comments
We present a perceptual model for evaluating results from color transfer methods. We conduct a user study, which provides a set of subjective scores for triples of input, target and result images. Then, for each triple, we compute a number of image features, which objectively characterize a color transfer. To describe the relationship between these features and the subjective scores, we build a regression model with random forests. An analysis and a cross-validation show that the predictions of our model are highly accurate.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views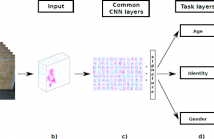
- Read more about DEEP MULTI-TASK LEARNING FOR GAIT-BASED BIOMETRICS
- Log in to post comments
The task of identifying people by the way they walk is known as ‘gait recognition’. Although gait is mainly used for identification, additional tasks as gender recognition or age estimation may be addressed based on gait as well. In such cases, traditional approaches consider those tasks as independent ones, defining separated task-specific features and models for them.
- Categories:
 94 Views
94 Views- Read more about FLEXIBLE 3D NEIGHBORHOOD CASCADE DEFORMABLE PART MODELS FOR OBJECT DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Cascade Deformable Part Models (DPMs) are cascade frameworks to speed up Deformable Part Models (DPMs), which are one of the state-of-the-art solutions for object detection. Its idea is to reject most non-object hypotheses from the early stages of detection process. By investigating the dependency between hypotheses over scales, we introduce a novel pruning method to accelerate Cascade DPM frameworks.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about FAST AND ACCURATE IMAGE RECOGNITION USING DEEPLY-FUSED BRANCHY NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
In order to achieve higher accuracy of image recognition, deeper and wider networks have been used. However, when the network size gets bigger, its forward inference time also takes longer. To address this problem, we propose Deeply-Fused Branchy Network (DFB-Net) by adding small but complete side branches to the target baseline main branch. DFB-Net allows easy-to-discriminate samples to be classified faster. For hard-to-discriminate samples, DFB-Net makes probability fusion by averaging softmax probabilities to make collaborative predictions.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views- Read more about ADAPTIVE CASCADE THRESHOLD LEARNING FROM NEGATIVE SAMPLES FOR DEFORMABLE PART MODELS
- Log in to post comments
A solution to deploy object detection systems to practical applications is to build cascade frameworks which do threshold comparisons in each stage to efficiently discard a large number of negative objects. For particular applications, these thresholds should be retrained for better effectiveness and the efficiency via training datasets. It means that we have to store labeled datasets permanently or collect huge data (for highquality thresholds) whenever learning new thresholds. Both approaches are inconvenient and expensive in terms of memory and data collection cost.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about Persistent Multiple Hypothesis Tracking for Wide Area Motion Imagery
- Log in to post comments
Wide area motion imagery (WAMI) acquired by an airborne sensor enables continuous monitoring of large urban areas. Reliable vehicle tracking in this imagery remains challenging due to low frame rate and small object size. Many approaches solely rely on motion detections provided by frame differencing or background subtraction. Recent approaches for persistent tracking, i.e. tracking vehicles even if they become stationary, compensate for missing motion detections by combining a detection-based tracker with a second tracker based on appearance or local context.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about Fast Template Matching for Intra Prediction
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views