
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
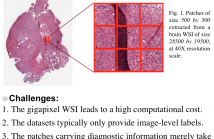
- Read more about WHOLE SLIDE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION VIA ITERATIVE PATCH LABELLING
- Log in to post comments
Brain tumor can be a fatal disease in the world. With the aim of improving survival rates, many computerized algorithms have been proposed to assist the pathologists to make a diagnosis, using Whole Slide Pathology Images (WSI). Most methods focus on performing patch-level classification and aggregating the patch-level results to obtain the image classification. Since not all patches carry diagnostic information, it is thus important for our algorithm to recognize discriminative and non-discriminative patches.
- Categories:
 184 Views
184 Views
- Read more about Image Fusion and Reconstruction of Compressed Data: A Joint Approach
- Log in to post comments
In the context of data fusion, pansharpening refers to the combination of a panchromatic (PAN) and a multispectral (MS) image, aimed at generating an image that features both the high spatial resolution of the former and high spectral diversity of the latter.
In this work we present a model to jointly solve the problem of data fusion and reconstruction of a compressed image; the latter is envisioned to be generated solely with optical on-board instruments, and stored in place of the original sources.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Automatic Optic Disk and Cup Segmentation of Fundus Images Using Deep Learning
- Log in to post comments
• To automatically segment optic disk (OD) and cup regions in fundus images to derive clinical parameters, such as, cup-to-disk diameter ratio (CDR), to assist glaucoma diagnosis. An eye fundus camera is non-invasive and low-cost,
enabling the screening of a large number of patients quickly.
• Discuss various strategies on how to leverage multiple doctor annotations and prioritize pixels belonging to different regions during network optimization.
• Evaluate proposed approaches on the Drishti-GS dataset.
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views

Image noise filters usually assume noise as white Gaussian. However, in a capturing pipeline, noise often becomes spatially correlated due to in-camera processing that aims to suppress the noise and increase the compression rate. Mostly, only high-frequency noise components are suppressed since the image signal is more likely to appear in the low-frequency components of the captured image. As a result, noise emerges as coarse grain which makes white (all-pass) noise filters ineffective, especially when the resolution of the target display is lower than the captured image.
- Categories:
 155 Views
155 Views
This paper addresses the problem of 3D human pose estimation when not all body parts are present in the input image, i.e., when some body joints are present while other joints are fully absent (we exclude self-occlusion). State-of-the-art is not designed and thus not effective for such cases. We propose a deep CNN to regress the human pose directly from an input image; we design and train this network to work under partial body presence. Parallel to this, we train a detection network to classify the presence or absence of each of the main body joints in the input image.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
This paper addresses the problem of 3D human pose estimation when not all body parts are present in the input image, i.e., when some body joints are present while other joints are fully absent (we exclude self-occlusion). State-of-the-art is not designed and thus not effective for such cases. We propose a deep CNN to regress the human pose directly from an input image; we design and train this network to work under partial body presence. Parallel to this, we train a detection network to classify the presence or absence of each of the main body joints in the input image.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
Object tracking is an active research area and numerous
techniques have been proposed recently. To evaluate a new
tracker, its performance is compared against existing ones
typically by averaging its quality based on a performance
measure, over all test video sequences. Such averaging is,
however, not representative as it does not account for outliers
(or similarities) between trackers. This paper presents a
framework for scoring and ranking of trackers using uncorrelated
quality metrics (overlap ratio and failure rate), coupled
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Background Light Estimation For Depth-dependent Underwater Image Restoration
- Log in to post comments
Light undergoes a wavelength-dependent attenuation and loses energy along its propagation path in water. In particular, the absorption of red wavelengths is greater than that of green and blue wavelengths in open ocean waters. This reduces the red intensity of the scene radiance reaching the camera and results in non-uniform light, known as background light, due to the scene depth. Restoration methods that compensate for this colour loss often assume constant background light and distort the colour of the water region(s).
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views