
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about INDOOR DENSE DEPTH MAP AT DRONE HOVERING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about AN INTERACTIVE CONTENT-BASED 3D SHAPE RETRIEVAL SYSTEM FOR ON-SITE CULTURAL HERITAGE ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we analyse the process of designing a Content-
Based 3D shape Retrieval (CB3DR) adapted for non-experts.
Our CB3DR solution aims at scanning an object on the fly
with a low-cost 3D sensor and retrieve similar shapes from
a database using the 3D point cloud acquired. Our system
should meet the requirements of archaeologists who would
like to be able to acquire artefacts without prior expertise in
scanning, then query easily from the field knowledge bases
for Cultural Heritage, and thus retrieve artefacts (i.e. objects
Icip2018.pptx
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about An Online Algorithm for Constrained Face Clustering in Videos
- Log in to post comments
This is the poster for the ICIP 2018 paper titled "An Online Algorithm for Constrained Face Clustering in Videos".
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about IMPROVING LIDAR DEPTH RESOLUTION WITH DITHER
- Log in to post comments
Using detector arrays can speed up lidar systems by parallelizing acquisition.
However, current SPAD arrays have time bins longer than
typical laser pulse durations, resulting in measurement errors dominated
by quantization. We propose an optical time-of-flight system
that uses subtractive dither to improve image depth resolution.
Modeling the measurement noise with a generalized Gaussian distribution
further improves estimation error in simulations, although
model mismatch prevents the same advantage for our experimental
- Categories:
 118 Views
118 Views
- Read more about THE COUPLED TUFF-BFF ALGORITHM FOR AUTOMATIC 3D SEGMENTATION OF MICROGLIA
- Log in to post comments
We propose an automatic 3D segmentation algorithm for multiphoton microscopy images of microglia. Our method is capable of segmenting tubular and blob-like structures from noisy images. Current segmentation techniques and software fail to capture the fine processes and soma of the microglia cells, useful for the study of the microglia role in the brain during healthy and diseased states. Our coupled tubularity flow field (TuFF)-blob flow field (BFF) method evolves a level set towards the object boundary using the directional tubularity and blobness measure of 3D images.
icip18.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about SEQUENTIAL RECOGNITION OF MANIPULATION ACTIONS USING DISCRIMINATIVE SUPERPIXEL GROUP MINING
- Log in to post comments
Activities such as those involved in food preparation involve interactions between hands, tools and multiple manipulated objects that affect them in visually complex ways making recognition of their constituent actions challenging. We describe a system that classifies action classes in such a setting based on discriminative spatio-temporal superpixel groups. The entire system operates sequentially enabling online action recognition. We obtain state-of-the-art results whilst employing a compact, interpretable representation.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about IMPROVING THE VISUAL QUALITY OF GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORK (GAN)-GENERATED IMAGES USING THE MULTI-SCALE STRUCTURAL SIMILARITY INDEX
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a simple yet effective method to improve the visual quality of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) generated images. In typical GAN architectures, the discriminator block is designed mainly to capture the class-specific content from images without explicitly imposing constraints on the visual quality of the generated images. A key insight from the image quality assessment literature is that natural scenes possess a very unique local structural and (hence) statistical signature, and that distortions affect this signature.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about SUPERRESOLUTION CONTOUR RECONSTRUCTION APPROACH TO A LINEAR THERMAL EXPANSION MEASUREMENT
- Log in to post comments
Optical imaging delivers absolute, non-contact, and high-dynamic-range measurement of thermal expansion. However, to achieve high accuracy, various factors should be accounted within the image analysis, including: image spatial sampling, lens aberrations, brightness nonuniformity and object edge deformations. Approach based on the object contour reconstruction is presented. Measurement procedure consists of two stages. Firstly, object edge contours corresponding to different temperatures are estimated.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about IMAGE SPLICING DETECTION THROUGH ILLUMINATION INCONSISTENCIES AND DEEP LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Fake news and deep fakes have been making social and mainstream media headlines. At the same time, engaged scientists strive for find- ing ways to detect forgeries and suspicious manipulations using even the subtlest clues. In this vein, this work proposes a new method for detecting photographic splicing by bringing together the high repre- sentation power of Illuminant Maps and Convolutional Neural Net- works as a way of learning directly from available training data the most important hints of a forgery.
- Categories:
 148 Views
148 Views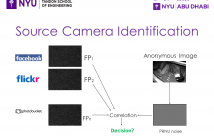
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views