
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
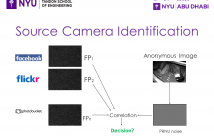
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
PRNU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity)-based camera fingerprints are useful for identifying the source camera of an anonymous image. As the query image has to be correlated with each candidate camera fingerprint, one key concern of this approach is the high run time overhead when using a large camera database. Clever techniques have been proposed to reduce the computation and I/O time either by reducing the size of the fingerprint or by group testing where multiple candidate fingerprints can be eliminated by a single correlation operation.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Feature Dimensionality Reduction with Graph Embedding and Generalized Hamming Distance
- Log in to post comments
Principal component analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) are the most well-known methods to reduce the dimensionality of feature vectors. However, both methods face challenges when used on multilabel data—each data point may be associated to multiple labels. PCA does not take advantage of label information thus the performance is sacrificed. LDA can exploit class information for multiclass data, but cannot be directly applied to multilabel problems. In this paper, we propose a novel dimensionality reduction method for multilabel data.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about DEEP MATCH TRACKER: CLASSIFYING WHEN DISSIMILAR, SIMILARITY MATCHING WHEN NOT
- Log in to post comments
Visual tracking frameworks employing Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown state-of-the-art performance due to their hierarchical feature representation. While classification and update based deep neural net tracking have shown good performance in terms of accuracy, they have poor tracking speed. On the other hand, recent matching based techniques using CNNs show higher than real-time speed in tracking but this speed is achieved at a considerably lower accuracy.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about SEMI-BLIND SPATIALLY-VARIANT DECONVOLUTION IN OPTICAL MICROSCOPY WITH LOCAL POINT SPREAD FUNCTION ESTIMATION BY USE OF CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
We present a semi-blind, spatially-variant deconvolution technique aimed at optical microscopy that combines a local estimation step of the point spread function (PSF) and deconvolution using a spatially variant, regularized Richardson-Lucy algorithm. To find the local PSF map in a computationally tractable way, we train a convolutional neural network to perform regression of an optical parametric model on synthetically blurred image patches.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about A HYBRID PRIOR MODEL FOR TUNABLE DIODE LASER ABSORPTION TOMOGRAPHY
- Log in to post comments
Model based methods have gained popularity in the past few decades in reconstruction problems particularly when the measurement data is sparse. In model based inference, apart from a model for the measurements, there exists a model for the unknown signal to be reconstructed, called the prior model. Model based methods tend to do very well when the prior model is accurate and representative of real world behavior of the unknown signal.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about IMPROVED PAIRWISE PIXEL-VALUE-ORDERING FOR HIGH-FIDELITY REVERSIBLE DATA HIDING
- Log in to post comments
Pixel-value-ordering (PVO) appears as an efficient technique for high-fidelity reversible data hiding. This paper proposes a reversible data hiding scheme based on the pairwise PVO framework with improved difference equations. Both the pixel pair selection and the embedding algorithms are also streamlined. The proposed scheme uses a block classification approach based on a local complexity metric. Uniform blocks are processed using the proposed improved pairwise PVO algorithm. Slightly noisy blocks are embedded using a classic PVO scheme and noisy blocks are kept unchanged.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about SEMI-SUPERVISED LEARNING OF CAMERA MOTION FROM A BLURRED IMAGE
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of camera motion estimation from a single blurred image with the aid of deep convolutional neural networks.
Unlike learning-based prior works that estimate a space-invariant blur kernel, we solve for the global camera motion which in turn
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about REVERSIBLE DATA HIDING IN ENCRYPTED COLOR IMAGES BASED ON VACATING ROOM AFTER ENCRYPTION AND PIXEL PREDICTION
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a new vacating room after encryption reversible data hiding scheme developed for color images. The proposed scheme uses standard exclusive-or encryption and inherits the main features of vacating room after encryption schemes, namely joint and separate methods for data embedding. The proposed scheme exploits both the correlation between neighboring pixels and the correlation between color channels by predicting the original pixel values on color channel differences.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views