
The 19th IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, SPAWC 2018, will be held in Kalamata, Greece, June 25-28, 2018. The workshop is devoted to advances in signal processing for wireless communications, networking, and information theory. The technical program features plenary talks, tutorials, as well as invited and contributed papers presented in poster format.

- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views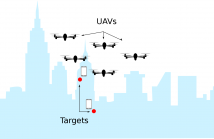
- Read more about Collaborative Target-Localization and Information-based Control in Networks of UAVs
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we study the capacity of UAV networks for high-accuracy localization of targets. We address the problem of designing a distributed control scheme for UAV navigation and formation based on an information-seeking criterion maximizing the target localization accuracy. Each UAV is assumed to be able to communicate and collaborate with other UAVs that are within a neighboring region, allowing for a feasible distributed solution which takes into account a trade-off between localization accuracy and speed of convergence to a suitable localization of the target.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about Can Hardware Distortion Correlation be Neglected When Analyzing Uplink SE in Massive MIMO?
- Log in to post comments
This paper analyzes how the distortion created by hardware impairments in a multiple-antenna base station affects the uplink spectral efficiency (SE), with focus on Massive MIMO. The distortion is correlated across the antennas, but has been often approximated as uncorrelated to facilitate (tractable) SE analysis. To determine when this approximation is accurate, basic properties of the distortion correlation are first uncovered.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about A Weighted Kernel-based Hierarchical Classification Method for Zoning of Sensors in Indoor Wireless Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views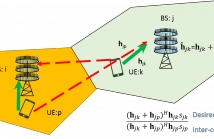
- Read more about Pilot Contamination in Massive MIMO: A Measurement-based Analysis using 2D-MUSIC
- Log in to post comments
When a base station (BS) sees desired and interfering
users at different angles, it results in non-overlapping angleof-
arrival (AoA) regions for those users. This is important for
reducing pilot contamination (PC) of massive MIMO systems.
Most state of the art studies utilize a simple non-line-of-sight
(NLoS) one-ring model which assumes sparse support and can
reasonably schedule users with different AoA to minimize PC.
However, it is not confirmed with measurements that the one-ring
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Random Access Schemes in Wireless Systems With Correlated User Activity
- Log in to post comments
Traditional random access schemes are designed based on the aggregate process of user activation, which is created on the basis of independent activations of the users. However, in Machine-Type Communications (MTC), some users are likely to exhibit a high degree of correlation, e.g. because they observe the same physical phenomenon. This paves the way to devise access schemes that combine scheduling and random access, which is the topic of this work. The underlying idea is to schedule highly correlated users in such a way that their transmissions are less likely to result in a collision.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Dynamic power Allocation for Smart Grids via ADMM
- Log in to post comments
spawc2018.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about SPAWC18 - ADAPTIVE PSK MODULATION SCHEME IN THE PRESENCE OF PHASE NOISE
- Log in to post comments
Phase noise is one of the major impairments affecting severely performance of millimeter-waves (mmWaves) systems. This paper addresses the problem of link adaption for coherent and non-coherent phase modulated signals subject to phase noise. In contrast to usual link adaptation techniques, we propose a scheme exploiting an estimation of not only the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) but also of the phase noise variance, which is essential to achieve reliable communications.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Resource Allocation for Solar Powered UAV Communication Systems
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the resource allocation design for multicarrier (MC) systems employing a solar powered unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) for providing communication services to multiple downlink users. We study the joint design of the three-dimensional positioning of the UAV and the power and subcarrier allocation for maximization of the system sum throughput. The algorithm design is formulated as a mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem, which requires a prohibitive computational complexity for obtaining the globally optimal solution.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views