
The 19th IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, SPAWC 2018, will be held in Kalamata, Greece, June 25-28, 2018. The workshop is devoted to advances in signal processing for wireless communications, networking, and information theory. The technical program features plenary talks, tutorials, as well as invited and contributed papers presented in poster format.

- Read more about Maximization of the Sum of Energy-Efficiency For Type-I HARQ Under The Rician Channel
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 1 Views
1 Views
- Read more about Statistical Analysis of EH Battery State under Noisy Energy Arrivals
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views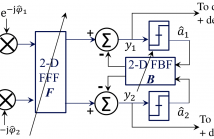
- Read more about Interference and Phase Noise Mitigation in a Dual-Polarized Faster-than-Nyquist Transmission
- Log in to post comments
Dual-polarized (DP) faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) transmission using higher-order modulation (HoM) schemes can significantly increase the spectral efficiency (SE) of the existing wireless backhaul links. However, FTN transmissions introduce inter-symbol interference (ISI), antenna polarization multiplexing suffers from cross-polarization interference (XPI) and HoM makes a communication system vulnerable to phase noise (PN) distortions.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about On the Age of Information in Multi-Source Multi-Hop Wireless Status Update Networks
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies a multi-source “age of information”
problem in multi-hop wireless networks with packetized
status updates and explicit channel contention. Specifically, the
scenario considered in this paper assumes that each node in the
network is a both a source and a monitor of information. Nodes
take turns broadcasting their information to other nodes in the
network while also maintaining tables of status updates for the
information received from all other nodes in the network. Lower
- Categories:
 127 Views
127 Views

- Read more about Distributed Scheduling Algorithms for Optimizing Information Freshness in Wireless Networks
- Log in to post comments
Age of Information (AoI), measures the time elapsed since the last received information packet was generated at the source. We consider the problem of AoI minimization for single-hop flows in a wireless network, under pairwise interference constraints and time varying channel. We consider simple, yet broad, class of distributed scheduling policies, in which a transmission is attempted over each link with a certain attempt probability. We obtain an interesting relation between the optimal attempt probability and the optimal AoI of the link, and its neighboring links.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views
- Read more about Self-Adaptive Energy Efficient Operation in UAV-assisted Public Safety Networks
- Log in to post comments
Public Safety Networks (PSN) are expected to provide resilient communication paradigms under disaster recovery scenarios. Towards providing an energy efficient solution an UAV-supported multi-level architecture is employed where user equipments (UEs) are grouped together in clusters.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Coordinated Hybrid Precoding for Energy-efficient Millimeter Wave Systems
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Rate-Splitting for Multi-group Multicast Beamforming in Multicarrier Systems
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we consider multi-group multicast transmissions with different types of service messages in an overloaded multicarrier system, where the number of transmitter antennas is insufficient to mitigate all inter-group interference. We show that employing a rate-splitting based multiuser beamforming approach enables a simultaneous delivery of the multiple service messages over the same time-frequency resources in a non-orthogonal fashion.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Communication efficient coreset sampling for distributed learning
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, distributed learning is studied using the approach of coreset. In the context of classification, an algorithm of coreset construction is proposed to reduce the redundancy of data and thus the communication requirement, similarly to source coding in traditional data communications. It is shown that the coreset based boosting has a high convergence rate and small sample complexity. Moreover, it is robust to adversary distribution, thus leading to potential applications in distributed learning systems.
poster_v.pdf
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views