
The 19th IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, SPAWC 2018, will be held in Kalamata, Greece, June 25-28, 2018. The workshop is devoted to advances in signal processing for wireless communications, networking, and information theory. The technical program features plenary talks, tutorials, as well as invited and contributed papers presented in poster format.

- Read more about A Fair Comparison of Virtual to Full Antenna Array Measurements
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about User Scheduling in Massive MIMO
- Log in to post comments
Massive MIMO relies on nearly orthogonal user channels to achieve unprecedented spectral efficiency. But in LoS (line-of-sight) environment, some users can be subjected to similar channel vectors. Serving users with similar channel vectors simultaneously can severely compromise the throughput performance to all users. We propose a scheduler that identifies users with similar channels and serves them in separate time slots with properly assigned data rates, while aiming to provide fair service to all users and maximize the system spectral efficiency at the same time.
- Categories:
 193 Views
193 Views
- Read more about Deterministic Annealing for Hybrid Beamforming Design in Multi-Cell MU-MIMO Systems
- Log in to post comments
Abstract—This work deals with hybrid beamforming (HBF)
for the MIMO Interfering Broadcast Channel (IBC), i.e. the
Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) Multi-User (MU) Multi-Cell
downlink channel. HBF is a low complexity alternative to fully
digital precoding in Massive MIMO systems. Hybrid architectures
involve a combination of digital and analog processing that
enables both beamforming and multiplexing gains. We consider
BF design by maximizing the Weighted Sum Rate (WSR) for
the case of Perfect Channel State Information at the Transmitter
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Ultrasonically Rechargeable Platforms for Closed-Loop Distributed Sensing and Actuation in the Human Body
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
- Read more about Analysis of the Viterbi Algorithm Using Tropical Algebra and Geometry
- Log in to post comments
The Viterbi algorithm and its pruning variant, are some of the most frequently used algorithms in communications and speech recognition. There has been extended research on improving the algorithms’ computational complexity, however work trying to interpret their nonlinear structure and geometry has been limited. In this work we analyse the Viterbi algorithm in the field of tropical (min-plus) algebra, and we utilize its pruning variant in order to define a polytope. Then, we interpret certain faces of the polytope as the most probable states of the algorithm.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Mobile App User Choice Engineering using Behavioral Science Models
- Log in to post comments
When interacting with mobile apps, users need to take decisions and make certain choices out of a set of alternative ones offered by the app. We introduce optimization problems through which we engineer the choices presented to users so that they are nudged towards decisions that lead to better outcomes for them and for the app platform. User decision-making rules are modeled by using principles from behavioral science and machine learning.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views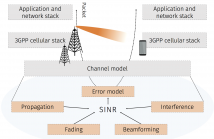
- Read more about Impact of Channel Models on the End-to-End Performance of mmWave Cellular Networks
- Log in to post comments
Communication at mmWave frequencies is one of the major innovations of the fifth generation of cellular networks, because of the potential multi-gigabit data rate given by the large amounts of available bandwidth. The mmWave channel, however, makes reliable communications particularly challenging, given the harsh propagation environment and the sensitivity to blockage. Therefore, proper modeling of the mmWave channel is fundamental for accurate results in system simulations of mmWave cellular networks.
spawc-poster-v1.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Flexible Infrastructure for the Development and Integration of Access / Fronthauling Solutions in Future Wireless Systems
- Log in to post comments
The deployment of the 5G technology(ies) is planned to start by 2020, and these future systems will comprise multiple heterogeneous technologies and services ranging from the personal cellular, wireless local area networks (WLAN) up to the Internet of Things (IoT). The inherent complexity and heterogeneity in technology conjugated with the random nature of both the wireless channel, access and services will make the system evaluation of 5G a very difficult task calling for flexible testbeds where the randomness of the radio environment and mobility can be realistically emulated.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Beyond PKI: Enhanced Authentication in Vehicular Networks via MIMO
- Log in to post comments
spawc_18.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about On Deep Learning-based Massive MIMO Indoor User Localization
- Log in to post comments
We examine the usability of deep neural networks for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) user positioning solely based on the orthogonal frequency division multiplex (OFDM) complex channel coefficients. In contrast to other indoor positioning systems (IPSs), the proposed method does not require any additional piloting overhead or any other changes in the communications system itself as it is deployed on top of an existing OFDM MIMO system. Supported by actual measurements, we are mainly interested in the more challenging non-line of sight (NLoS) scenario.
- Categories:
 70 Views
70 Views