
The 19th IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, SPAWC 2018, will be held in Kalamata, Greece, June 25-28, 2018. The workshop is devoted to advances in signal processing for wireless communications, networking, and information theory. The technical program features plenary talks, tutorials, as well as invited and contributed papers presented in poster format.

- Read more about Mirror-Prox SCA Algorithm for Multicast Beamforming and Antenna Selection
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers the (NP-)hard problem of joint multicast beamforming and antenna selection. Prior work has focused on using Semi-Definite relaxation (SDR) techniques in an attempt to obtain a high-quality sub-optimal solution. However, SDR suffers from the drawback of having high computational complexity, as SDR lifts the problem to higher dimensional space, effectively squaring the number of variables.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Deep Tree Models for ‘Big’ Biological Data
- Log in to post comments
The identification of useful temporal dependence structure in discrete time series data is an important component of algorithms applied to many tasks in statistical inference and machine learning, and used in a wide variety of problems across the spectrum of biological studies. Most of the early statistical approaches were ineffective in practice, because the amount of data required for reliable modelling grew exponentially with memory length.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
Using information about the wireless communica- tion channel is a well known approach to estimate a users position. So far it has been shown that such methods can provide positioning information in line-of-sight (LOS) situations by estimating channel properties like time of flight, direction of arrival, and direction of departure of a link between a single access point and station. In this paper we focus on mmWave channels and propose a method that allows positioning in indoor scenarios even under non-line-of-sight conditions by exploiting the presence of scatterers.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about Multi-Antenna Receiver for Ambient Backscatter Communication Systems
- Log in to post comments
Consider an ambient modulated backscatter communication (AmBC) system adopting binary phase shift keying modulation that the receiver is to decode the backscatter device induced message without knowledge of the channel state information, the statistical channel covariance matrices, and the noise variance at the receiver antennas. In this paper, we apply the fact that the ambient orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) signals with a large number of subcarriers contain repetitive elements inducing time correlation.
SPAWC18.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
The transceiver separations required for synthesizing full rank MIMO matrices in line of sight (LoS) geometries scale as the square root of the product of carrier wavelength
and range. The wavelengths at millimeter (mm) wave carrier frequencies are small therefore enable LoS spatial multiplexing with practical node form factors at ranges of 10-100 m, depending on the carrier frequency. However, such LoS MIMO links become frequency selective even with small geometric mismatches. Exact channel inversion in an
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Artificial Interference Aided Physical Layer Security in Cache-enabled Heterogeneous Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Distributed Inference over Multitask Graphs under Smoothness
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Distributed Inference over Multitask Graphs under Smoothness
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views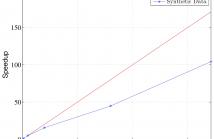
- Read more about NESTEROV-BASED ALTERNATING OPTIMIZATION FOR NONNEGATIVE TENSOR COMPLETION: ALGORITHM AND PARALLEL IMPLEMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of nonnegative tensor completion. Our aim is to derive an efficient algorithm that is also suitable for parallel implementation. We adopt the alternating optimization framework and solve each nonnegative matrix completion problem via a Nesterov-type algorithm for smooth convex problems. We describe a parallel implementation of the algorithm and measure the attained speedup in a multi-core computing environment. It turns out that the derived algorithm is an efficient candidate for the solution of very large-scale sparse nonnegative tensor completion problems.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views