
- Read more about SEMI-BLIND SPATIALLY-VARIANT DECONVOLUTION IN OPTICAL MICROSCOPY WITH LOCAL POINT SPREAD FUNCTION ESTIMATION BY USE OF CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
We present a semi-blind, spatially-variant deconvolution technique aimed at optical microscopy that combines a local estimation step of the point spread function (PSF) and deconvolution using a spatially variant, regularized Richardson-Lucy algorithm. To find the local PSF map in a computationally tractable way, we train a convolutional neural network to perform regression of an optical parametric model on synthetically blurred image patches.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about Radial function based ab-initio tomographic reconstruction for cryo electron microscopy
- Log in to post comments
Poster2018.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views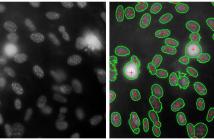
- Read more about CELL SEGMENTATION VIA REGION-BASED ELLIPSE FITTING
- Log in to post comments
We present a region based method for segmenting and splitting
images of cells in an automatic and unsupervised manner.
The detection of cell nuclei is based on the Bradley’s method.
False positives are automatically identified and rejected based
on shape and intensity features. Additionally, the proposed
method is able to automatically detect and split touching cells.
To do so, we employ a variant of a region based multi-ellipse
fitting method (DEFA) that makes use of constraints on the
- Categories:
 87 Views
87 Views
- Read more about OCT VOLUMETRIC DATA RESTORATION VIA PRIMAL-DUAL PLUG-AND-PLAY METHOD
- Log in to post comments
This work proposes a volumetric data restoration method, especially for data acquired through an optical coherence tomography (OCT) device. OCT is a technique for acquiring a tomographic image of a specimen object in a few $\mu$m scale by using a near infrared laser. The authors have been trying dynamic observation of epithelium in cochlear of the inner ear. Currently, there is a problem to remove the influence of the measurement process as well as noise due to image sensor sensitivity.
- Categories:
 148 Views
148 Views- Read more about BACT-3D: A LEVEL SET SEGMENTATION APPROACH FOR DENSE MULTI-LAYERED 3D BACTERIAL BIOFILMS
- Log in to post comments
In microscopy, new super-resolution methods are emerging that produce three-dimensional images at resolutions ten times smaller than that provided by traditional light microscopy. Such technology is enabling the exploration of structure and function in living tissues such as bacterial biofilms that have mysterious interconnections and organization. Unfortunately, the standard tools used in the image analysis community to perform segmentation and other higher-level analyses cannot be applied naively to these data.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Blur Estimation for Photon-Limited Images
- Log in to post comments
Blur estimation is critical to blind image deconvolution. In this work, by taking Gaussian kernel as an example, we propose an approach to estimate the blur size for photon-limited images. This estimation is based on the minimization of a novel criterion, blur-PURE (Poisson unbiased risk estimate), which makes use of the Poisson noise statistics of the measurement. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method in various scenarios.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views- Read more about A Two-Stage Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) based Clustering Algorithm for 2D Deformable Registration of Time Sequenced Images
- Log in to post comments
Significant cardiac and respiratory motion of the living subject, occasional spells of defocus, drifts in the field of view,
and long image sequences make the registration of in-vivo microscopy image sequences used in atherosclerosis study an
onerous task. In this study we developed and implemented a novel Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)-based clustering
method for image sequence registration that first constructs a minimum spanning tree for the input image sequence. The
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about IMAGE-BASED MEASUREMENT OF CARGO TRAFFIC FLOW IN COMPLEX NEURITE NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Neurons depend critically on active transport of cargoes throughout their complex neurite networks for their survival and function. Defects in this process have been strongly associated with many human neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases. To understand related neuronal physiology and disease mechanisms, it is essential to measure the traffic flow within the neurite networks. Currently, however, image analysis methods required for this measurement are lacking.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about A data-driven approach to feature space selection for robust micro-endoscopic image reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views