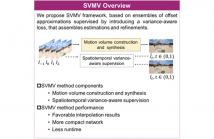
- Read more about SVMV: SPATIOTEMPORAL VARIANCE-SUPERVISED MOTION VOLUME FOR VIDEO FRAME INTERPOLATION
- Log in to post comments
High-performance video frame interpolation is challenging for complex scenes with diverse motion and occlusion characteristics. Existing methods, deploying off-the-shelf flow estimators to acquire initial characterizations refined by multiple subsequent models, often require heavy network architectures that are not practical for resource constrained systems. We investigate the unary potentials of the characterizations to improve efficiency.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views- Read more about Joint Unmixing And Demosaicing Methods For Snapshot Spectral Images
- Log in to post comments
Recent technological advances in design and processing speed have successfully demonstrated a new snapshot mosaic imaging sensor architecture (SSI), allowing miniaturized platforms to efficiently acquire the spatio-spectral content of the dynamic scenes from a single exposure. However, SSI systems have a fundamental trade-off between spatial and spectral resolution because they associate each pixel with a specific spectral band.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views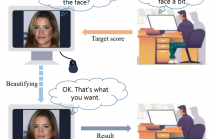
- Read more about CUSTOMIZED AUTOMATIC FACE BEAUTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
In the age of social media, posting attractive mugshots is commonplace, leading to an urgent need for automatic facial beautification techniques. To better meet the esthetic preferences of users, we devise a customized automatic face beautification task that can retouch the face adaptively to match the user-entered target score whilst preserving the ID information as much as possible. To accomplish this task, we propose a Human Esthetics Guided StyleGAN Inversion method to retouch each face in the embedding space using StyleGAN inversion.
video.pptx
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Towards Realizing the Value of Labeled Target Samples: a Two-Stage Approach for Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation (SSDA) is a recently emerging research topic that extends from the widely-investigated Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) by further having a few target samples labeled, i.e., the model is trained with labeled source samples, unlabeled target samples as well as a few labeled} target samples.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views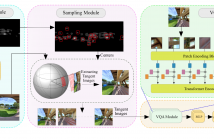
- Read more about ST360IQ: NO-REFERENCE OMNIDIRECTIONAL IMAGE QUALITY ASSESSMENT WITH SPHERICAL VISION TRANSFORMERS
- Log in to post comments
Omnidirectional images, aka 360 images, can deliver immersive and interactive visual experiences. As their popularity has increased dramatically in recent years, evaluating the quality of 360 images has become a problem of interest since it provides insights for capturing, transmitting, and consuming this new media. However, directly adapting quality assessment methods proposed for standard natural images for omnidirectional data poses certain challenges. These models need to deal with very high-resolution data and implicit distortions due to the spherical form of the images.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about DEEP LOW LIGHT IMAGE ENHANCEMENT VIA MULTI-SCALE RECURSIVE FEATURE ENHANCEMENT AND CURVE ADJUSTMENT
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Photographs taken in low-illumination environment have a low signal-to-noise ratio and impaired visual quality. Enhancing low-light images tends to amplify noise. To address this problem, we propose a Multi-Scale Recursive Feature Enhancement (MSRFE) network for low light image enhancement. The MSRFE network consists of several Feature Enhancement (FE) blocks which are applied to enhance the multi-scale image feature and remove the noise recursively in each scale residual map between adjacent scale feature.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views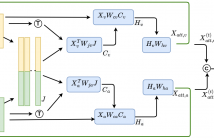
- Read more about Recursive Joint Attention for Audio-Visual Fusion in Regression-Based Emotion Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In video-based emotion recognition (ER), it is important to effectively leverage the complementary relationship among audio (A) and visual (V) modalities, while retaining the intramodal characteristics of individual modalities. In this paper, a recursive joint attention model is proposed along with long short-term memory (LSTM) modules for the fusion of vocal and facial expressions in regression-based ER.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about LIGHTWEIGHT PORTRAIT SEGMENTATION VIA EDGE-OPTIMIZED ATTENTION
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Multispectral image fusion based on super pixel segmentation
- Log in to post comments
Multispectral image fusion is a computer vision process that is essential to remote sensing. For applications such as dehazing and object detection, there is a need to offer solutions that can perform in real-time on any type of scene. Unfortunately, current state-of-the-art approaches do not meet these criteria as they need to be trained on domain-specific data and have high computational complexity. This paper focuses on the task of fusing color (RGB) and near-infrared (NIR) images as this the typical RGBT sensors, as in multispectral cameras for detection, fusion, and dehazing.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views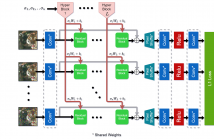
- Read more about Hypernetwork-based Adaptive Image Restoration
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Adaptive image restoration models can restore images with different degradation levels at inference time without the need to retrain the model. We present an approach that is highly accurate and allows a significant reduction in the number of parameters. In contrast to existing methods, our approach can restore images using a single fixed-size model, regardless of the number of degradation levels. On popular datasets, our approach yields state-of-the-art results in terms of size and accuracy for a variety of image restoration tasks, including denoising, deJPEG, and super-resolution.
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views