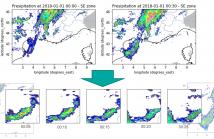
When providing the boundary conditions for hydrological flood models and estimating the associated risk, interpolating precipitation at very high temporal resolutions (e.g. 5 minutes) is essential not to miss the cause of flooding in local regions. In this paper, we study optical flow-based interpolation of globally available weather radar images from satellites.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
- Read more about Fine-Grained Dynamic Loss for Accurate Single-Image Super-Resolution
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about LEARNING TO FUSE HETEROGENEOUS FEATURES FOR LOW-LIGHT IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
In this paper, an approach to self-calibrate an outward-looking camera from camera images is presented. Ego lane boundaries are detected in the image frame. A straight line is fitted to each detected boundary. Vanishing point in image space is computed as the intersection of the fitted straight lines. A closed-form solution is obtained for camera pitch and yaw angles using vanishing points coordinates.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about BALANCED STRIPE-WISE PRUNING IN THE FILTER
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL, SPECTRAL AND GRAPH REPRESENTATIONS FOR VIDEO-BASED FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION IN CHILDREN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL, SPECTRAL AND GRAPH REPRESENTATIONS FOR VIDEO-BASED FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION IN CHILDREN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL, SPECTRAL AND GRAPH REPRESENTATIONS FOR VIDEO-BASED FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION IN CHILDREN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Extracting and Distilling Direction-adaptive Knowledge for Lightweight Object Ddetection in Remote Sensing Images
- Log in to post comments
Recently, some lightweight convolutional neural network (CNN) models have been proposed for airborne or spaceborne remote sensing object detection (RSOD) tasks. However, these lightweight detectors suffer from performance degradation due to the compromise of limited computing resources on embedded devices. In order to narrow this performance gap, a direction-adaptive knowledge extraction and distillation (DKED) method is proposed.
Poster_Paper8521.pdf
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Hyperspectral Image Super-resolution with Deep Priors and Degradation Model Inversion
- Log in to post comments
To overcome inherent hardware limitations of hyperspectral imaging systems with respect to their spatial resolution, fusion-based hyperspectral image (HSI) super-resolution is attracting increasing attention. This technique aims to fuse a low-resolution (LR) HSI and a conventional high-resolution (HR) RGB image in order to obtain an HR HSI. Recently, deep learning architectures have been used to address the HSI super-resolution problem and have achieved remarkable performance.
poster_wang.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views