
- Read more about Pondering about Task Spatial Misalignment: Classification-Localization Equilibrated Object Detection
- Log in to post comments
Object detection is a fundamental task in computer vision, consisting of both classification and localization tasks. Previous works mostly perform classification and localization with shared feature extractor like Convolution Neural Network. However, the tasks of classification and localization exhibit different sensitivities with regard to the same feature, hence the "task spatial misalignment" issue. This issue can result in a hedge issue between the performances of localizer and classifier.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views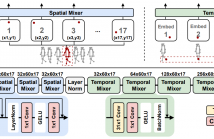
- Read more about GaitMixer: Skeleton-based Gait Representation Learning via Wide-spectrum Multi-axial Mixer
- Log in to post comments
Most existing gait recognition methods are appearance-based, which rely on the silhouettes extracted from the video data of human walking activities. The less-investigated skeleton-based gait recognition methods directly learn the gait dynamics from 2D/3D human skeleton sequences, which are theoretically more robust solutions in the presence of appearance changes caused by clothes, hairstyles, and carrying objects. However, the performance of skeleton-based solutions is still largely behind the appearance-based ones.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about (Supplementary Material) ABC: Attention with Bilinear Correlation for Infrared Small Target Detection
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about Applicability limitations of differentiable full-reference image-quality metrics
- Log in to post comments
Subjective image-quality measurement plays a critical role in the development of image- processing applications. The purpose of a visual-quality metric is to approximate the results of subjective assessment. In this regard, more and more metrics are under development, but little research has considered their limitations. This paper addresses that deficiency: we show how image preprocessing before compression can artificially increase the quality scores provided by the popular metrics DISTS, LPIPS, HaarPSI, and VIF as well as how these scores are inconsistent with subjective-quality scores.
DCC_pptx.pptx
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about Video Compression with Arbitrary Rescaling Network
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Most video platforms provide video streaming services with different qualities, and the resolution of the videos usually adjusts the quality of the services. So high-resolution videos need to be downsampled for compression. In order to solve the problem of video coding at different resolutions, we propose a rate-guided arbitrary rescaling network (RARN) for video resizing before encoding.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about Video Transformer based Video Quality Assessment with Spatiotemporally adaptive Token Selection and Assembly
- Log in to post comments
Video quality assessment (VQA) for user generated content (UGC) videos plays important role in video compression and processing. Convolutional neural network (CNN) based quality assessment for UGC is the research focus with inspiring model accuracy increment in the past three years. However, regularly temporal-sampling with temporal feature loss, as well as fixed token selection strategy video transformer (ViT) with insufficient representational capacity of tokens, jointly degrade the accuracy of conventional ViT based quality assessment.
- Categories:
 80 Views
80 Views
- Read more about VCSL: Video Compressive Sensing with Low-complexity ROI Detection in Compressed Domain
- Log in to post comments
By exploiting the potential of deep learning, video compressive sensing (CS) has achieved tremendous improvement recently. Due to the video CS is mainly served for the fixed scene in real life. In this paper, we propose a novel video compressive sensing with a low-complexity region-of-interest (ROI) detection method (VCSL). The ROI is located by calculating the difference between the reference frame and the following frames in our framework, which is compact without introducing any additional neural networks and parameters.
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
- Read more about Hierarchical Privacy-Preserving and Communication-Efficient Compression via Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Data collection and sharing have a tremendous impact on technology, business and society. Correspondingly, it brings in significant privacy and communication concerns. To this end, we present a hierarchical privacy-preserving and communication-efficient compression scheme via compressed sensing (CS) to address these two issues. In the encoding stage, the
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Automatic Defect Segmentation by Unsupervised Anomaly Learning
- Log in to post comments
This paper addresses the problem of defect segmentation in semiconductor manufacturing. The input of our segmentation is a scanning-electron-microscopy (SEM) image of the candidate defect region. We train a U-net shape network to segment defects using a dataset of clean background images. The samples of the training phase are produced automatically such that no manual labeling is required. To enrich the dataset of clean background samples, we apply defect implant augmentation. To that end, we apply a copy-and-paste of a random image patch in the clean specimen.
- Categories:
 324 Views
324 Views