
- Read more about VISUAL RELATIONSHIP RECOGNITION VIA LANGUAGE AND POSITION GUIDED ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
Visual relationship recognition, as a challenging task used to distinguish the interactions between object pairs, has received much attention recently. Considering the fact that most visual relationships are semantic concepts defined by human beings, there are many human knowledge, or priors, hidden in them, which haven’t been fully exploited by existing methods.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about Interactive Subjective Study on Picture-level Just Noticeable Difference of Compressed Stereoscopic Images
- Log in to post comments
The Just Noticeable Difference (JND) reveals the minimum distortion that the Human Visual System (HVS) can perceive. Traditional studies on JND mainly focus on background luminance adaptation and contrast masking. However, the HVS does not perceive visual content based on individual pixels or blocks, but on the entire image. In this work, we conduct an interactive subjective visual quality study on the Picture-level JND (PJND) of compressed stereo images. The study, which involves 48 subjects and 10 stereoscopic images compressed with H.265 intra coding and JPEG2000, includes two parts.
- Categories:
 145 Views
145 Views
Color Guided Depth image denoising often suffers from the texture coping from the color image as well as the blurry effect at the depth discontinuities. Motivated by this, we propose an optimized color-guided filter for depth image denoising from different types of noises. This is a new framework that helps to mitigate the texture coping and enhance the depth discontinuities, especially in heavy noises. This framework consists of two parts namely depth driven color flattening model and patch synthesis-based Markov random field model.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Video-Based, Occlusion-Robust Multi-View Stereo Using Inner-Boundary Depths of Textureless Areas
- Log in to post comments
Occlusions and poor textures are two main problems in multi-view stereo reconstruction. This paper presents a video-based solution to address both challenges in depth estimation. We focus on reconstructing accurate inner boundaries of visible textureless areas, particularly for occluded background, by leveraging the reliable depths of object edges. This is done by efficiently respecting two local cues with complementary advantages, i.e. smoothness and density of recovered surfaces.
ICASSP2019.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Transform Domain based Medical Image Super-Resolution via Deep Multi-scale Network
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a new medical image super-resolution (SR) network, namely deep multi-scale network (DMSN), in the uniform discrete curvelet transform (UDCT) domain. DMSN is made up of a set of cascaded multi-scale fushion (MSF) blocks. In each MSF block, we use convolution kernels of different sizes to adaptively detect the local multiscale feature, and then local residual learning (LRL) is used to learn effective feature from preceding MSF block and current multi-scale features.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
While neural networks have achieved vastly enhanced performance over traditional iterative methods in many cases, they are generally empirically designed and the underlying structures are difficult to interpret. The algorithm unrolling approach has helped connect iterative algorithms to neural network architectures. However, such connections have not been made yet for blind image deblurring. In this paper, we propose a neural network architecture that advances this idea.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about 3D VISUAL SPEECH ANIMATION USING 2D VIDEOS
- Log in to post comments
In visual speech animation, lip motion accuracy is of paramount importance for speech intelligibility, especially for the hard of hearing or foreign language learners. We present an approach for visual speech animation that uses tracked lip motion in front-view 2D videos of a real speaker to drive the lip motion of a synthetic 3D head. This makes use of a 3D morphable model (3DMM), built using 3D synthetic head poses, with corresponding landmarks identified in the 2D videos and the 3DMM.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about View-Invariant Action Recognition From RGB Data via 3D Pose Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel view-invariant action recognition method using a single monocular RGB camera. View-invariance remains a very challenging topic in 2D action recognition due to the lack of 3D information in RGB images. Most successful approaches make use of the concept of knowledge transfer by projecting 3D synthetic data to multiple viewpoints. Instead of relying on knowledge transfer, we propose to augment the RGB data by a third dimension by means of 3D skeleton estimation from 2D images using a CNN-based pose estimator.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views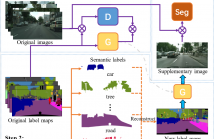
- Read more about Poster of pixel level data augmentation for semantic image segmentation using generative adversarial networks
- Log in to post comments
Semantic segmentation is one of the basic topics in computer vision, it aims to assign semantic labels to every pixel of an image. Unbalanced semantic label distribution could have a negative influence on segmentation accuracy. In this paper, we investigate using data augmentation approach to balance the label distribution in order to improve segmentation performance. We propose using generative adversarial networks (GANs) to generate realistic images for improving the performance of semantic segmentation networks.
- Categories:
 131 Views
131 Views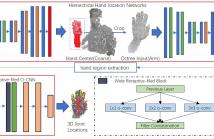
- Read more about A Novel Framework Of Hand Localization And Hand Pose Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel framework for hand localization and pose estimation from a single depth image. For hand localization, unlike most existing methods that using heuristic strategies, e.g. color segmentation, we propose Hierarchical Hand location Networks (HHLN) to estimate the hand location from coarse to fine in depth images, which is robust to the complex environment and efficient. It first applied at a low resolution octree of the whole depth image and produce coarse hand region and then constructs the hand region into a high resolution octree for fine location estimation.
poster_cheyunlong.pdf
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views