
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views
- Read more about Optimal Feature Selection for Blind Super-Resolution Image Quality Evaluation
- Log in to post comments
The visual quality of images resulting from Super Resolution (SR) techniques is predicted with blind image quality assessment (BIQA) models trained on a database(s) of human rated distorted images and associated human subjective opinion scores. Such opinion-aware (OA) methods need a large amount of training samples with associated human subjective scores, which are scarce in the field of SR. By contrast, opinion distortion unaware (ODU) methods do not need human subjective scores for training.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Scene Privacy Protection
- Log in to post comments
Uploading pictures to a cloud service may reveal, through automatic inference, scene information that a user might want to keep private. To protect images from automatic scene classification, we present a method that misleads the classifier while introducing only a minimal distortion and limiting the likelihood that the ground-truth class can be inferred from the processed image. The method, based on the Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM), generates adversarial images and leverages a multi-class scene classifier trained to select a target scene class.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Scenario Discovery for Crowd Counting
- Log in to post comments
Crowd counting, i.e., estimation number of the pedestrian in crowd images, is emerging as an important research problem
with the public security applications. A key component for the crowd counting systems is the construction of counting
models which are robust to various scenarios under facts such as camera perspective and physical barriers. In this paper,
we present an adaptive scenario discovery framework for crowd counting. The system is structured with two parallel
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views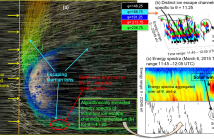
- Read more about Autonomous Detection and Disambiguation of Martian Ion Trails Using Geometric Signal Processing Techniques
- Log in to post comments
We present recently developed computational techniques that exploit spectral geometry of the energy spectra for differential energy flux over MAVEN data sets. The goal is to enable a large scale automated discovery detection of statistical analysis of ion trails in the Martian atmosphere. Specifically, we present a case study across a diverse portfolio of azimuthal (φ) and polar (θ) angles over the same time frame and demonstrate that angular separation helps us to distinguish between individual ion escape processes.
- Categories:
 68 Views
68 Views
- Read more about Blind Denoising of Mixed Gaussian-Impulse Noise by Single CNN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views
3D shape recognition has attracted a great interest in computer vision due to its large number of important and exciting applications. This has led to exploring a variety of approaches to develop more efficient 3D analysis methods. However, current works take into account descriptions of global shape to generate models, ignoring small differences causing the problem of mismatching, especially for high similarity shapes.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views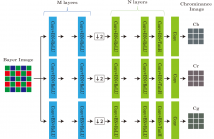
- Read more about IMAGE DEMOSAICKING VIA CHROMINANCE IMAGES WITH PARALLEL CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Many conventional demosaicking methods are based on hand-crafted filters. However, the filters yield false colors in salient regions like edges and textures. For acquisition of high quality images, we focus on neural networks. Neural networks lead to high accuracy in many fields. However, there are few methods in demosaicking field. For adaptation to demosaicking, we consider not only network's architecture but also the input. In this research, we utilize a Bayer image as input of our networks.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views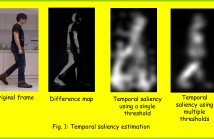
- Read more about Temporal Salience Based Human Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a new approach for human action recognition exploring the temporal salience. We exploit features over the temporal saliency maps for learning the action representation using a local dense descriptor. This approach automatically guides the descriptor towards the most interesting contents, i.e. the salience region, and obtains the action representation using solely the saliency information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views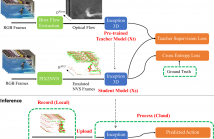
- Read more about NEUROMORPHIC VISION SENSING FOR CNN-BASED ACTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Neuromorphic vision sensing (NVS) hardware is now gaining traction as a low-power/high-speed visual sensing technology that circumvents the limitations of conventional active pixel sensing (APS) cameras. While object detection and tracking models have been investigated in conjunction with NVS, there is currently little work on NVS for higher-level semantic tasks, such as action recognition.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views