
- Read more about Dense Optical Flow for the Reconstruction of Weakly Textured and Structured Surfaces: Application to Endoscopy
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a structure from motion (SfM)-based surface reconstruction method for images including weak textures and structures. In SfM, the quality of the determination of homologous points between images plays a key role in terms of reconstruction performances. However, classical feature matching-based methods as integrated in the state-ofthe-art SfM algorithms are often inoperative for images with weak structures and textures. This contribution describes a dense optical flow-based solution enabling the point correspondence determination in such scenes.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about Learning Target-oriented Dual Attention for Robust RGB-T Tracking
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about Guided CycleGAN via Semi-Dual Optimal Transport for Photo-Realistic Face Super-resolution
- Log in to post comments
Face super-resolution has been studied for decades, and many approaches have been proposed to upsample low-resolution face images using information mined from paired low-resolution (LR) images and high-resolution (HR) images. However, most of this kind of works only simply sharpen the blurry edges in the upsampled face images and typically no photo-realistic face is reconstructed in the final result. In this paper, we present a GAN-based algorithm for face super-resolution which properly synthesizes photo-realistic super-recovered face.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views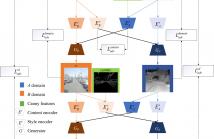
- Read more about CANNYGAN: Edge-PREserving image translation with disentangled features
- Log in to post comments
The image-to-image translation task often associates with the problem of missing texture and edge information. In this paper, we proposed a framework to translate images while preserving more realistic textures and details. To this end, we disentangle the samples into shared content space and domain-specific style domain. Then, according to the blurred outlines and textures in the source domain, we introduce the classic canny edge detection algorithm to encode the boundary and edge information in the content latent space.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about RANGE IMAGE BASED POINT CLOUD COLORIZATION USING CONDITIONAL GENERATIVE MODEL
- Log in to post comments
Nowadays, three-dimensional (3D) point cloud has been an emerging medium to represent real-world scenes and objects. However, there is a considerable proportion of point clouds whose color attribute information is not captured during the acquisition process due to the device or environment limitations. This poses a great challenge for efficient management and utilization of point clouds. To address this problem, we introduce an automatic colorization scheme based on a deep generative network for 3D point clouds.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about Recognizing Material of Covered Object: A Case Study with Graffiti
- Log in to post comments
Recognizing materials using image analysis is a classic problem. However, little research has been done with the images which have visual impediments such as noise, obstacle, or painting. This paper introduces the problem of recognizing covered materials which are distorted visually (e.g., materials covered by graffiti).
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
This document includes the slides of the ICIP2019 presentation of the publication "DVDnet: A Fast Network for Deep Video Denoising".
- Categories:
 148 Views
148 Views
- Read more about EFFICIENT FINE-TUNING OF NEURAL NETWORKS FOR ARTIFACT REMOVAL IN DEEP LEARNING FOR INVERSE IMAGING PROBLEMS
- Log in to post comments
While Deep Neural Networks trained for solving inverse imaging problems (such as super-resolution, denoising, or inpainting tasks) regularly achieve new state-of-the-art restoration performance, this increase in performance is often accompanied with undesired artifacts generated in their solution. These artifacts are usually specific to the type of neural network architecture, training, or test input image used for the inverse imaging problem at hand. In this paper, we propose a fast, efficient post-processing method for reducing these artifacts.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
This paper explores the modeling and exploitation of semi-local similarity in natural images to address the ill-posed nature of image interpolation. Our approach distinguishes itself from prior approaches by direct and careful use of semi-local similar patches to interpolate each individual patch. Our work uses a simple, parallelizable algorithm without the need to solve complicated optimization problems. Experimental results demonstrate that our interpolated images achieve significantly higher objective and subjective quality compared with those from state-of-the-art algorithms.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about ON THE PERFORMANCE OF DIBR METHODS WHEN USING DEPTH MAPS FROM STATE-OF-THE-ART STEREO MATCHING ALGORITHMS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we compare the quality of synthesized views produced by four DIBR methods when fed by depth maps estimated by five state-of-the-art stereo matching algorithms. Also, we compute the correlation between four popular metrics for ranking stereo matching algorithms and two metrics commonly used to evaluate synthesized views (PSNR and SSIM) plus one specific for DIBR.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views