


- Read more about DISCOVER THE EFFECTIVE STRATEGY FOR FACE RECOGNITION MODEL COMPRESSION BY IMPROVED KNOWLEDGE DISTILLATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about DISCOVER THE EFFECTIVE STRATEGY FOR FACE RECOGNITION MODEL COMPRESSION BY IMPROVED KNOWLEDGE DISTILLATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about SIGPORT FOR THE 2018 IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON IMAGE PROCESSING (ICIP) for paper 1630
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about SIGPORT FOR THE 2018 IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON IMAGE PROCESSING (ICIP) for paper 1630
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about CONDITIONAL DISTRIBUTION LEARNING WITH NEURAL NETWORKS AND ITS APPLICATION TO UNIVERSAL IMAGE DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
A simple and scalable denoising algorithm is proposed that can be applied to a wide range of source and noise models. At the core of the proposed CUDE algorithm is symbol-by-symbol universal denoising used by the celebrated DUDE algorithm, whereby the optimal estimate of the source from an unknown distribution is computed by inverting the empirical distribution of the noisy observation sequence by a deep neural network, which naturally and implicitly aggregates multiple contexts of similar characteristics and estimates the conditional distribution more accurately.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Normal Similarity Network for Generative Modelling
- Log in to post comments
icip (2).pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about TOTAL VARIATION REGULARIZED REWEIGHTED LOW-RANK TENSOR COMPLETION FOR COLOR IMAGE INPAINTING
- Log in to post comments
Recent low-rank based tensor completion (LRTC) algorithms have been successfully applied into color image inpainting. However, most of existing LRTC algorithms treat each dimension of tensors equally, which ignores the differences of the intrinsic structure correlations among dimensions. In this paper, we make a detailed analysis about the rank properties of each dimension and design a simple yet effective reweighted low-rank tensor completion model that truthfully capture the intrinsic structure correlations with reduced computational burden.
ICIP183018.pdf
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views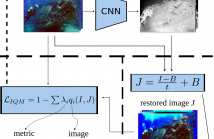
- Read more about Visual-Quality-driven Learning for Underwater Vision Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
The image processing community has witnessed remarkable advances in enhancing and restoring images. Nevertheless, restoring the visual quality of underwater images remains a great challenge. End-to-end frameworks might fail to enhance the visual quality of underwater images since in several scenarios it is not feasible to provide the ground truth of the scene radiance. In this work, we propose a CNN-based approach that does not require ground truth data since it uses a set of image quality metrics to guide the restoration learning process.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views