
- Read more about 100+ Times Faster Video Completion by Optical-Flow-Guided Variational Refinement
- Log in to post comments
Despite the higher video-completion quality that recently proposed methods have enabled for a wide variety of cases, their computational complexity remains a major concern. These methods typically frame video completion as an optimization problem over the whole spatiotemporal domain—a problem that is expensive to solve both in time and space. In this paper we propose a lighter-weight multipass video-completion pipeline that replaces global spatiotemporal optimization with simpler frame-by-frame motion reconstruction and refinement.
ICIP_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views

Material aging has a significant effect on the realistic rendering of artwork objects. Small deformations of the surface structure, color or texture variations contribute to the realistic look of artwork objects. These aging effects depend on material composition, object usage, weathering conditions, and a large number of other physical, biological, and chemical parameters.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Co-segmentation of Non-homogeneous Image Sets
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we formulate image co-segmentation as a classification problem in an unsupervised framework with the classes being the common foreground and the remaining regions in the image set. We first find a set of superpixels across all images with high feature similarity such that the constituent superpixels in individual images are spatially compact and label them as seed for the common foreground. Those superpixels with high background probability are labeled as respective seeds for multiple background classes.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about MOVING-CAMERA VIDEO SURVEILLANCE IN CLUTTERED ENVIRONMENTS USING DEEP FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
This paper deals with the challenging problem of visual anomaly detection in a cluttered environment using videos acquired with a moving camera. The anomalies considered are abandoned objects.
A new method is proposed for comparing two videos (an anomalyfree reference video and a target one possibly with anomalies) by
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Automatic ISP Image Quality Tuning Using Non-linear Optimization
- Log in to post comments
Image Signal Processor (ISP) comprises of various blocks to reconstruct image sensor raw data to final image consumed by human visual system or computer vision applications. Each block typically has many tuning parameters due to the complexity of the operation. These need to be hand tuned by Image Quality (IQ) experts, which takes considerable amount of time. In this paper, we present an automatic IQ tuning using nonlinear optimization and automatic reference generation algorithms.
- Categories:
 136 Views
136 Views
- Read more about A STUDY OF SUBJECTIVE VIDEO QUALITY AT VARIOUS SPATIAL RESOLUTIONS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Poster - Topological Eulerian Synthesis of Slow Motion Periodic Videos
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of taking a video that is comprised of multiple periods of repetitive motion, and reordering the frames of the video into a single period, producing a detailed, single cycle video of motion. This problem is challenging, as such videos often contain noise, drift due to camera motion and from cycle to cycle, and irrelevant background motion/occlusions, and these factors can confound the relevant periodic motion we seek in the video.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views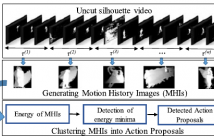
- Read more about PMHI: Proposals From Motion History Images for Temporal Segmentation of Long Uncut Videos
- Log in to post comments
This letter proposes a method for the generation of temporal action proposals for the segmentation of long uncut video sequences. The presence of consecutive multiple actions in video sequences makes the temporal segmentation a challenging problem due to the unconstrained nature of actions in space and time. To address this issue, we exploit the nonaction segments present between the actual human actions in uncut videos. From the long uncut video, we compute the energy of consecutive nonoverlapping motion history images (MHIs), which provides spatiotemporal information of motion.
poster_SPL.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views