
Inverse problems appear in many applications, such as image deblurring and inpainting. The common approach to address them is to design a specific algorithm for each problem. The Plug-and-Play (P&P) framework, which has been recently introduced, allows solving general inverse problems by leveraging the impressive capabilities of existing denoising algorithms. While this fresh strategy has found many applications, a burdensome parameter tuning is often required in order to obtain high-quality results.
- Categories:
 1617 Views
1617 Views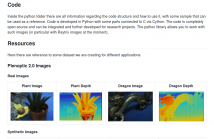
- Read more about Plenoptic Toolbox 2.0 - Benchmarking of Depth Estimation Methods for MLA-Based Focused Plenoptic Cameras
- Log in to post comments
MLA-based focused plenoptic cameras, also called type 2.0 cameras, have advantages over type 1.0 plenoptic cameras, because of their better inherent spatial image resolution and their compromise between depth of focus and angular resolution. However, they are more difficult to process since they require a depth estimation first to compute the all-in-focus image from the raw MLA image data. Current toolboxes for plenoptic cameras only support the type 1.0 cameras (like Lytro) and cannot handle type 2.0 cameras (like Raytrix).
- Categories:
 113 Views
113 Views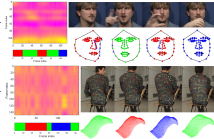
- Read more about DEFORMABLE MOTION 3D RECONSTRUCTION BY UNION OF REGULARIZED SUBSPACES
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an approach to jointly retrieve camera pose, time-varying 3D shape, and automatic clustering based on motion primitives, from incomplete 2D trajectories in a monocular video. We introduce the concept of order-varying temporal regularization in order to exploit video data, that can be indistinctly applied to the 3D shape evolution as well as to the similarities between images. This results in a union of regularized subspaces which effectively encodes the 3D shape deformation.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
Image deblurring is one of the standard problems in image processing.
Recently, this area of research is dominated by blind deblurring, where neither the sharp image nor the blur are known.
The majority of works, however, target scenarios where the captured scene is static and the blur is caused by camera motion, i.e. the whole image is blurred.
In this work we address a similar yet different scenario: an object moves in front of a static background.
Such object is blurred due to motion while the background is sharp and partially occluded by the object.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Anisotropic Partial Differential Equation based Video Saliency Detection
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel video saliency detection method using the Partial Differential Equations (PDEs). We first form a static adaptive anisotropic PDE model from the unpredicted frames of the video using a detection map and a saliency seeds set of most attractive image elements. At the same time, we also extract motion features from the predicted frames of the video to generate motion saliency map. Then, we combine these two maps to obtain the final saliency map (video).
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about AN ADVANCED VISIBILITY RESTORATION TECHNIQUE FOR UNDERWATER IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about MARGIN-EMBEDDING CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS WITH FEATURE SELECTION FOR PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is a classical subspace learning method of capturing the common semantic information underlying multi-view data. It has been used in person re-identification (re-ID) task by treating the task of matching identical individuals across non-overlapping multi-cameras as a multi-view learning problem. However, CCA-based re-ID methods still achieve unsatisfactory results because few jointly consider discriminative margin information and selecting importantly relevant features.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views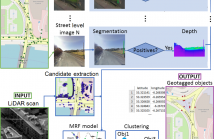
Abundant image and sensory data collected over the last decades represents an invaluable source of information for cataloging and monitoring of the environment. Fusion of heterogeneous data sources is a challenging but promising tool to efficiently leverage such information. In this work we propose a pipeline for automatic detection and geolocation of recurring stationary objects deployed on fusion scenario of street level imagery and LiDAR point cloud data. The objects are geolocated coherently using a fusion procedure formalized as a Markov random field problem.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
Most outdoor vision systems can be influenced by rainy weather conditions. In this paper, we address a rain removal problem from a single image. Some existing de-raining methods suffer from hue change due to neglect of the information in low frequency layer. Others fail in assuming enough rainy image models. To solve them, we propose a residual deep network architecture called ResDerainNet. Based on the deep convolutional neural network (CNN), we learn the mapping relationship between rainy and residual images from data.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
Most outdoor vision systems can be influenced by rainy weather conditions. In this paper, we address a rain removal problem from a single image. Some existing de-raining methods suffer from hue change due to neglect of the information in low frequency layer. Others fail in assuming enough rainy image models. To solve them, we propose a residual deep network architecture called ResDerainNet. Based on the deep convolutional neural network (CNN), we learn the mapping relationship between rainy and residual images from data.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views