
- Read more about DEPTH ESTIMATION NETWORK FOR DUAL DEFOCUSED IMAGES WITH DIFFERENT DEPTH-OF-FIELD
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose an algorithm to estimate the depth map of a scene using defocused images. In particular, the depth map is estimated using two defocused images with different depth-of-field for the same scene. Similar to the approach of the general depth from defocus (DFD), the proposed algorithm obtains the depth information from the
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about Class-specific Coders for Hyper-spectral Image Classification
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we introduce the paradigm of class specific
coders (CSC) for classification of hyperspectral images
(HSI). Apparently, CSC are defined as a set of distinct
encoder-decoder (henceforth called a coder) networks where
a given coder is trained on the samples of a particular class.
In contrast to auto-encoders (AE) which learn an identity
mapping of data in an unsupervised fashion, the CSC model,
on the other hand, learns re-constructive mappings for all
possible pairs of training samples for each class in separate
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about IMAGE STITCHING FOR DUAL FISHEYE CAMERAS
- Log in to post comments
Panoramic photography creates stunning immersive visual experiences for viewers. In this paper, we investigate how to seamlessly stitch a pair of images captured by two uncalibrated, back-to-back, 195-degree fisheye cameras to generate a surround view of a 3D scene. It is a challenging task because the two camera centers are displaced and because the common region is the most distorted area. To enhance the robustness of feature matching and hence the quality of stitching, we propose a novel technique that projects the image rectilinearly onto an equirectangular plane.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 142 Views
142 Views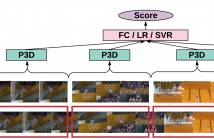
- Read more about S3D: Stacking Segmental P3D for Action Quality Assessment
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Action quality assessment is crucial in areas of sports, surgery and assembly line where action skills can be evaluated. In this paper, we propose the Segment-based P3D-fused network S3D built-upon ED-TCN and push the performance on the UNLV-Dive dataset by a significant margin. We verify that segment-aware training performs better than full-video training which turns out to focus on the water spray. We show that temporal segmentation can be embedded with few efforts.
- Categories:
 107 Views
107 Views
- Read more about DENSE BYNET: RESIDUAL DENSE NETWORK FOR IMAGE SUPER RESOLUTION
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a method, Dense ByNet, for single image super-resolution based on a convolutional neural network (CNN). The main innovation is a new architecture that combines several CNN design choices. Using a residual network as a basis, it introduces dense connections inside residual blocks, significantly reducing the number of parameters. Second, we apply dilation convolutions to increase the spatial context. Lastly, we propose modifications to the activation and cost functions.
- Categories:
 104 Views
104 Views
- Read more about SuperCut: Superpixel Based Foreground Extraction With Loose Bounding Boxes in One Cutting
- Log in to post comments
Interactive image segmentation that uses a bounding box containing the foreground has gained great popularity because of its convenience. However, its performance is often degraded when the bounding box is not tight enough or covers large background regions. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a novel segmentation algorithm called ``SuperCut". This algorithm provides robust segmentation in one cut even with loose bounding boxes.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about How Should We Handle 4D Light Fields with CNNs?
- Log in to post comments
We investigated how we should handle high dimensional light fields (LFs) with convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
An LF is a 4-D signal representation of light rays, and it is interpreted as a set of dense multi-view images.
As an important building block of various light field applications, we focused on signal restoration problems for LFs, and we adopted CNNs as the solver for them because of its striking performance on the conventional 2-D images.
In applying CNNs, the high dimensionality of LFs should be carefully addressed.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about CHANGING BACKGROUND TO FOREGROUND: AN AUGMENTATION METHOD BASED ON CONDITIONAL GENERATIVE NETWORK FOR STINGRAY DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Image processing has been a popular tool for biological researches. Detecting specific animals in aerial images captured by an UAV is a crucial research topic. As the rapid progress of deep learning (DL), it has been a popular approach to many image classification and object detection tasks. However, DL usually requires a large set of training samples to learn the network weights, while the biological image materials are often insufficient to fulfill the demand.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Double Complete D-LBP with Extreme Learning Machine Auto-Encoder and Cascade Forest for Facial Expression Analysis
- Log in to post comments
Although the obtained accuracy on some lab-controlled facial expression datasets has been very high, the recognition of facial expressions in wild environments is still a challenging problem. Local Binary Patterns (LBP) is a widely used operator in facial expression recognition. However, there are few variations of LBP operators specifically designed for facial expression recognition. In this paper, we propose a novel representation approach called the Double Complete d-LBP (Double Cd-LBP) according to the characteristics of facial expressions.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views