- Read more about ON DNN POSTERIOR PROBABILITY COMBINATION IN MULTI-STREAM SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR REVERBERANT ENVIRONMENTS
- Log in to post comments
A multi-stream framework with deep neural network (DNN) classifiers has been applied in this paper to improve automatic speech recognition (ASR) performance in environments with different reverberation characteristics. We propose a room parameter estimation model to determine the stream weights for DNN posterior probability combination with the aim of obtaining reliable log-likelihoods for decoding. The model is implemented by training a multi-layer
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about Statistical Normalisation of Phase-based Feature Representation for Robust Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In earlier work we have proposed a source-filter decomposition of
speech through phase-based processing. The decomposition leads
to novel speech features that are extracted from the filter component
of the phase spectrum. This paper analyses this spectrum and the
proposed representation by evaluating statistical properties at vari-
ous points along the parametrisation pipeline. We show that speech
phase spectrum has a bell-shaped distribution which is in contrast to
the uniform assumption that is usually made. It is demonstrated that
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about A Speaker-Dependent Deep Learning Approach to Joint Speech Separation and Acoustic Modeling for Multi-Talker Automatic Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel speaker-dependent (SD) approach to joint training of deep neural networks (DNNs) with an explicit speech separation structure for multi-talker speech recognition in a single-channel setting. First, a multi-condition training strategy is designed for a SD-DNN recognizer in multi-talker scenarios, which can significantly reduce the decoding runtime and improve the recognition accuracy over the approaches that use speaker-independent DNN models with a complicated joint decoding framework.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views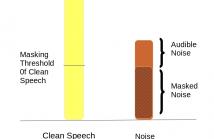
- Read more about Vector Taylor Series Expansion with Auditory Masking for Noise Robust Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of speech recognition in
the presence of additive noise. We investigate the applicability
and efficacy of auditory masking in devising a robust front end
for noisy features. This is achieved by introducing a masking
factor into the Vector Taylor Series (VTS) equations. The resultant
first order VTS approximation is used to compensate the parameters
of a clean speech model and a Minimum Mean Square
Error (MMSE) estimate is used to estimate the clean speech
Paper17_BD.pdf
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views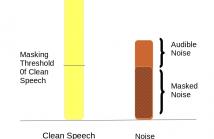
- Read more about Vector Taylor Series Expansion with Auditory Masking for Noise Robust Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of speech recognition in
the presence of additive noise. We investigate the applicability
and efficacy of auditory masking in devising a robust front end
for noisy features. This is achieved by introducing a masking
factor into the Vector Taylor Series (VTS) equations. The resultant
first order VTS approximation is used to compensate the parameters
of a clean speech model and a Minimum Mean Square
Error (MMSE) estimate is used to estimate the clean speech
Paper17_BD.pdf
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Two-Stage Noise Aware Training Using Asymmetric Deep Denoising Autoencoder
- Log in to post comments
Ever since the deep neural network (DNN)-based acoustic model appeared, the recognition performance of automatic peech recognition has been greatly improved. Due to this achievement, various researches on DNN-based technique for noise robustness are also in progress. Among these approaches, the noise-aware training (NAT) technique which aims to improve the inherent robustness of DNN using noise estimates has shown remarkable performance. However, despite the great performance, we cannot be certain whether NAT is an optimal method for sufficiently utilizing the inherent robustness of DNN.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views- Read more about SPEECH EMOTION RECOGNITION USING TRANSFER NON-NEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORIZATION
- Log in to post comments
In practical situations, the emotional speech utterances are often collected from different devices and conditions, which will obviously affect the recognition performance. To address this issue, in this paper, a novel transfer non-negative matrix factorization (TNMF) method is presented for cross-corpus speech emotion recognition. First, the NMF algorithm is adopted to learn a latent common feature space for the source and target datasets.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 ViewsPages
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4