This study introduces a machine hearing system for robot audition, which enables a robotic agent to pro-actively minimize the uncertainty of sound source location estimates through motion. The proposed system is based on an active exploration approach, providing a means to model and predict effects of the agent's future motions on localization uncertainty in a probabilistic manner. Particle filtering is used to estimate the posterior probability density function of the source position from binaural measurements, enabling to jointly assess azimuth and distance of the source.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Distributed Sequence Prediction: A consensus+innovations approach
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on the problem of distributed sequence
prediction in a network of sparsely interconnected agents,
where agents collaborate to achieve provably reasonable
predictive performance. An expert assisted online learning
algorithm in a distributed setup of the consensus+innovations
form is proposed, in which the agents update their weights
for the experts’ predictions by simultaneously processing the
latest network losses (innovations) and the cumulative losses
obtained from neighboring agents (consensus). This paper
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 ViewsWe consider the problem of quickly detecting an abrupt change of linear coefficients in linear regression models. In particular, the observer sequentially observes a sequence of observations $\{ (x_n; y_n) \}_{n=1}^{\infty}$, which is assumed to obey a linear regression model at each time slot n. Some of the coefficients in the linear model change at a fixed but unknown time $t$. The post-change linear coefficients are unknown to the observer. The observer aims to design an online algorithm to detect the model change based on his sequential observations.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about Kernel-based low-rank feature extraction on a budget for Big data streams
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about GlobalSIP_slides_AEK
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers unconstrained convex optimiza- tion problems with time-varying objective functions. We propose algorithms with a discrete time-sampling scheme to find and track the solution trajectory based on prediction and correction steps, while sampling the problem data at a constant rate of 1{h, where h is the length of the sampling interval. The prediction step is derived by analyzing the iso-residual dynamics of the optimality conditions.
globalsip.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A Sequential Bayesian Inference Framework for Blind Frequency Offset Estimation
- Log in to post comments
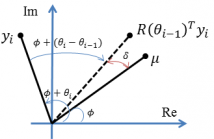
Precise estimation of synchronization parameters is essential for reliable
data detection in digital communications and phase errors can
result in significant performance degradation. The literature on estimation
of synchronization parameters, including the carrier frequency
offset, are based on approximations or heuristics because
the optimal estimation problem is analytically intractable for most
cases of interest. We develop an online Bayesian inference procedure
for blind estimation of the frequency offset, for arbitrary signal
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 ViewsPages
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4