- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about SAMPLING AND DISTORTION TRADEOFFS FOR INDIRECT SOURCE RETRIEVAL
- Log in to post comments
We study the problem of remote reconstruction of a continuous signal from its multiple corrupted versions. We are interested in the optimal number of samples and their locations for each corrupted signal to minimize the total reconstruction distortion of the remote signal. The correlation among the corrupted signals can be utilized to reduce the sampling rate.
Poster3.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views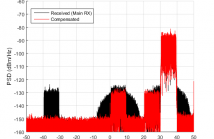
- Read more about REFERENCE RECEIVER ENABLED DIGITAL CANCELLATION OF NONLINEAR OUT-OF-BAND BLOCKER DISTORTION IN WIDEBAND RECEIVERS
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes digital cancellation of nonlinear distortion originating from out-of-band blocking carriers and induced by the analog front-end nonlinearities in direct-conversion receivers (RXs). The cancellation is enabled by employing an additional reference RX for capturing these blockers. In addition, cancellation of mirror-frequency interference is targeted. The feed-forward cancellation of nonlinear distortion is blindly adaptive without any a priori information of the received signal or the nonlinearity characteristics of the RX.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Beam Tracking for Mobile Millimeter Wave Communication Systems
- Log in to post comments
Millimeter wave (mmWave) is an attractive option for high data rate applications. Enabling mmWave communications requires appropriate beamforming, which is conventionally realized by a lengthy beam training process. Such beam training will be a challenge for applying mmWave to mobile environments. As a solution, a beam tracking method requiring to train only one beam pair to track a path in the analog beamforming architecture is developed. Considering its low complexity which is suitable for mobile settings, the extended Kalman filter is chosen as the tracking filter.
- Categories:
 265 Views
265 Views
- Read more about Blind Digital Modulation Classification based on M-th Power nonlinear Transformation
- Log in to post comments
Automatic Modulation Classification (AMC) has received a major attention last decades, as a required step between signal detection and demodulation. In the fully-blind scenario, this task turns out to be quite challenging, especially when the computational complexity and the robustness to uncertainty matter. AMC commonly relies on a preprocessor whose function is to estimate unknown parameters, filter the received signal and sample it in a suitable way. Any preprocessing error inherently leads to a performance loss.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views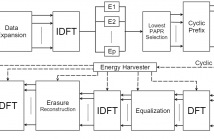
- Read more about Self-Sustainable OFDM Transmissions with Smooth Energy Delivery
- Log in to post comments
Transmitting energy and information simultaneously using orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) to obtain receiver energy self-sufficiency has recently been proposed.To obtain smooth energy delivery, this project analyzes a new architecture for self-sustainable OFDM transmissions that reduces the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) in the cyclic prefix through a frame-theoretic operation that modifies the erasure pattern selection technique.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views- Read more about Performance Analysis for Pilot-based 1-bit Channel Estimation with Unknown Quantization Threshold
- Log in to post comments
Parameter estimation using quantized observations is of importance in many practical applications. Under a symmetric 1-bit setup, consisting of a zero-threshold hard limiter, it is well known that the large sample performance loss for low signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) is moderate (2/pi or -1.96dB). This makes low-complexity analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) with 1-bit resolution a promising solution for future wireless communications and signal processing devices.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views- Read more about Kalman Filters with Bayesian Quadratic Game Fusion in Networks
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 Views
Views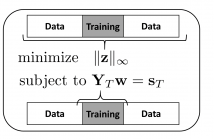
- Read more about Compressed Training Adaptive Equalization
- Log in to post comments
We introduce it compressed training adaptive equalization as a novel approach for reducing number of training symbols in a communication packet. The proposed semi-blind approach is based on the exploitation of the special magnitude boundedness of communication symbols. The algorithms are derived from a special convex optimization setting based on l_\infty norm. The corresponding framework has a direct link with the compressive sensing literature established by invoking the duality between l_1 and l_\infty norms.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 ViewsWe address the transmission of bivariate Gaussian sources using analog Joint Source Channel Coding (JSCC). The analog mappings are specifically designed to exploit the correlation between the source symbols. A parametric mapping based on sinusoidal functions is proposed and its performance is compared to that of the optimal non parametric mappings and other applicable analog JSCC mappings, and also to the theoretical bound.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views