
- Read more about Time shifted PCA based cue extraction for stereo audio signals (poster)
- Log in to post comments
In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, one of the key issues is to decompose a signal into cue and ambient components based on their spatial features. Principal component analysis (PCA) has been widely employed in cue extraction. However, the performance of PCA based cue extraction is highly dependent on the assumptions of the input signal model. One of these assumptions is the input signal contains highly correlated cue at zero lag. However, this assumption is often unmet.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Time shifted PCA based cue extraction for stereo audio signals
- Log in to post comments
In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, one of the key issues is to decompose a signal into cue and ambient components based on their spatial features. Principal component analysis (PCA) has been widely employed in cue extraction. However, the performance of PCA based cue extraction is highly dependent on the assumptions of the input signal model. One of these assumptions is the input signal contains highly correlated cue at zero lag. However, this assumption is often unmet.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Linear estimation based primary-ambient extraction for stereo audio signals (slides)
- Log in to post comments
Audio signals for moving pictures and video games are often linear combinations of primary and ambient components. In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, these mixed signals are usually decomposed into primary and ambient components to facilitate flexible spatial rendering and enhancement. Existing approaches such as principal component analysis (PCA) and least squares (LS) are widely used to perform this decomposition from stereo signals.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views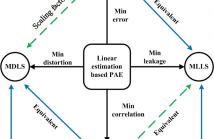
- Read more about Linear estimation based primary-ambient extraction for stereo audio signals
- Log in to post comments
Audio signals for moving pictures and video games are often linear combinations of primary and ambient components. In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, these mixed signals are usually decomposed into primary and ambient components to facilitate flexible spatial rendering and enhancement. Existing approaches such as principal component analysis (PCA) and least squares (LS) are widely used to perform this decomposition from stereo signals.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views