- Read more about Channel estimation for crosstalk cancellation in wireless acoustic networks
- Log in to post comments
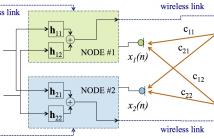
In this paper we deal with the estimation of the room impulse response (RIR) between each loudspeaker and each microphone of a wireless acoustic network of two nodes when used to implement a crosstalk canceller. The nodes of the network are commercial devices connected via standard wireless links, presenting low computational requirements and non-ideal synchronization between them. Moreover, the nodes can exchange information, but they cannot share their signals due to the high throughput and perfect synchronism that would be required.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about INTERAURAL TIME DELAY PERSONALISATION USING INCOMPLETE HEAD SCANS
- Log in to post comments
When using a set of generic head-related transfer functions (HRTFs) for spatial sound rendering, personalisation can be considered to minimise localisation errors. This typically involves tuning the characteristics of the HRTFs or a parametric model according to the listener’s anthropometry. However, measuring anthropometric features directly remains a challenge in practical applications, and the mapping between anthropometric and acoustic features is an open research problem.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about FREQUENCY-BASED CUSTOMIZATION OF MULTIZONE SOUND SYSTEM DESIGN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 Views
Views- Read more about FREQUENCY-BASED CUSTOMIZATION OF MULTIZONE SOUND SYSTEM DESIGN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views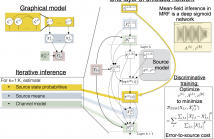
- Read more about Deep Unfolding for Multichannel Source Separation
- Log in to post comments
Deep unfolding has recently been proposed to derive novel deep network architectures from model-based approaches. In this paper, we consider its application to multichannel source separation. We unfold a multichannel Gaussian mixture model (MCGMM), resulting in a deep MCGMM computational network that directly processes complex-valued frequency-domain multichannel audio and has an architecture defined explicitly by a generative model, thus combining the advantages of deep networks and model-based approaches.
- Categories:
 195 Views
195 Views- Read more about Informed Direction of Arrival Estimation using a Spherical-Head Model for Hearing Aid Applications
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Improving Speech Privacy in Personal Sound Zones
- Log in to post comments
This work proposes two methods for providing speech privacy between spatial zones in anechoic and reverberant environments. The methods are based on masking the content leaked between regions. The masking is optimised to maximise the speech intelligibility contrast (SIC) between the zones. The first method uses a uniform masker signal that is combined with desired multizone loudspeaker signals and requires acoustic contrast between zones.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views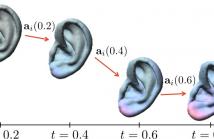
- Read more about Generating a Morphable Model of Ears
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes the generation of a morphable model for external ear shapes. The aim for the morphable model is to characterize an ear shape using only a few parameters in order to assist the study of morphoacoustics. The model is derived from a statistical analysis of a population of 58 ears from the SYMARE database. It is based upon the framework of large deformation diffeomorphic metric mapping (LDDMM) and the vector space that is constructed over the space of initial momentums describing the diffeomorphic transformations.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Spatial Audio Reproduction using Primary Ambient Extraction (PhD thesis slides)
- Log in to post comments
Spatial audio reproduction is essential to create a natural listening experience for digital media. Majority of the legacy audio contents are in channel-based format, which is very particular on the desired playback system. Considering the diversity of today’s playback systems, the quality of reproduced sound scenes degrades significantly when mismatches between the audio content and the playback system occur.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Spatial Audio Reproduction using Primary Ambient Extraction (PhD thesis)
- Log in to post comments
Spatial audio reproduction is essential to create a natural listening experience for digital media. Majority of the legacy audio contents are in channel-based format, which is very particular on the desired playback system. Considering the diversity of today’s playback systems, the quality of reproduced sound scenes degrades significantly when mismatches between the audio content and the playback system occur.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views