
- Read more about Joint source localization and dereverberation by sound field interpolation using sparse regularizations (slides)
- Log in to post comments
n this paper, source localization and dereverberation are formulated jointly as an inverse problem. The inverse problem consists in the interpolation of the sound field measured by a set of microphones by matching the recorded sound pressure with that of a particular acoustic model. This model is based on a collection of equivalent sources creating either spherical or plane waves. In order to achieve meaningful results, spatial, spatio-temporal and spatio-spectral sparsity can be promoted in the signals originating from the equivalent sources.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCE OF ULTRASONIC TRANSDUCERS FOR PARAMETRIC ARRAY LOUDSPEAKER
- Log in to post comments
A parametric array loudspeaker (PAL) consists of a lot of ultrasonic transducers in most cases and is driven by an ultrasonic which is modulated by audible sound. Because each ultrasonic transducer has each difference resonant frequency, there is the individual difference in ultrasonic transducers of a PAL in a manufacturing process. In this paper, two PALs are made of each set of transducers with large and small variance of resonant frequencies.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views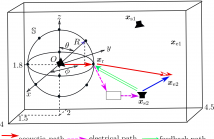
- Read more about Reference Signal Generation for Broadband ANC Systems in Reverberant Rooms
- Log in to post comments
One major issue of implementing broadband active noise control systems in reverberant
rooms is the lack of reference signals. In this work, by exploiting the spatial sound
field characteristics, a time-domain sound field separation method is developed to
generate the reference signal for broadband active noise control systems in reverberant
rooms. The time-domain sound field separation method separates the outgoing field produced
by the primary source from the secondary source feedback and room reverberation on a
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views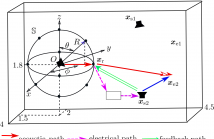
- Read more about Reference Signal Generation for Broadband ANC Systems in Reverberant Rooms
- Log in to post comments
One major issue of implementing broadband active noise control systems in reverberant
rooms is the lack of reference signals. In this work, by exploiting the spatial sound
field characteristics, a time-domain sound field separation method is developed to
generate the reference signal for broadband active noise control systems in reverberant
rooms. The time-domain sound field separation method separates the outgoing field produced
by the primary source from the secondary source feedback and room reverberation on a
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about PERCEPTUALLY MOTIVATED ANALYSIS OF NUMERICALLY SIMULATED HEAD-RELATED TRANSFER FUNCTIONS GENERATED BY VARIOUS 3D SURFACE SCANNING SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Numerical simulations offer a feasible alternative to the direct acoustic measurement of individual head-related transfer functions (HRTFs). For the acquisition of high quality 3D surface scans, as required for these simulations, several approaches exist. In this paper, we systematically analyze the variations between different approaches and evaluate the influence of the accuracy of 3D scans on the resulting simulated HRTFs. To assess this effect, HRTFs were numerically simulated based on 3D scans of the head and pinna of the FABIAN dummy head generated with 6 different methods.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Time of Arrival Disambiguation Using the Linear Radon Transform
- Log in to post comments
Echo labeling, the challenging task of assigning acoustic reflections to image sources, is equivalent to the highly-important disambiguation task in room geometry inference. A method using the Radon transform, an image processing tool, is proposed to address this challenge. The method relies on acoustic wavefront detection in room impulse response stacks, obtained with a uniform linear array of loudspeakers and one microphone. We show in our experiments that the proposed method can both label and detect echoes.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views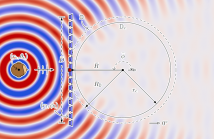
- Read more about Active Speech Control using Wave-Domain Processing with a Linear Wall of Dipole Secondary Sources
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the effects of compensating for wave-domain filtering delay in an active speech control system. An active control system utilising wave-domain processed basis functions is evaluated for a linear array of dipole secondary sources. The target control soundfield is matched in a least squares sense using orthogonal wavefields to a predicted future target soundfield. Filtering is implemented using a block-based short-time signal processing approach which induces an inherent delay.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views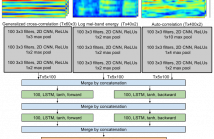
- Read more about Sound Event Detection Using Spatial Features and Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views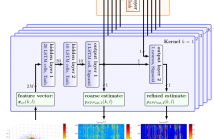
- Read more about DNN-based Speech Mask Estimation for Eigenvector Beamforming
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views