- Read more about Fast continuous HRTF acquisition with unconstrained movements of human subjects
- Log in to post comments
Head related transfer function (HRTF) is widely used in 3D audio reproduction, especially over headphones. Conventionally, HRTF database is acquired at discrete directions and the acquisition process is time-consuming. Recent works have been proposed to improve HRTF acquisition efficiency via continuous acquisition. However, these HRTF acquisition techniques still require subject to sit still (with limited head movement) in a rotating chair. In this paper, we further relax the head movement constraint during acquisition by using a head tracker.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Tutorial: Assisted Listening for headphones and hearing aids: Signal Processing Techniques
- Log in to post comments
With the strong growth of the mobile devices and emerging virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications, headsets are becoming more and more preferable in personal listening due to its convenience and portability. Assistive listening (AL) devices like hearing aids have seen much advancement. Creating a natural and authentic listening experience is the common objective of these VR, AR, and AL applications. In this tutorial, we will present state-of-the-art audio and acoustic signal processing techniques to enhance the sound reproduction in headsets and hearing aids.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Applying Primary Ambient Extraction for Immersive Spatial Audio Reproduction [slides]
- Log in to post comments
Spatial audio reproduction is essential to create a natural listening experience for digital media. Majority of the legacy audio contents are in channel-based format, which is very particular on the desired playback system. Considering the diversity of today's playback systems, the quality of reproduced sound scenes degrades significantly when mismatches between the audio content and the playback system occur. An active sound control approach is required to take the playback system into consideration.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Applying Primary Ambient Extraction for Immersive Spatial Audio Reproduction
- Log in to post comments
Spatial audio reproduction is essential to create a natural listening experience for digital media. Majority of the legacy audio contents are in channel-based format, which is very particular on the desired playback system. Considering the diversity of today's playback systems, the quality of reproduced sound scenes degrades significantly when mismatches between the audio content and the playback system occur. An active sound control approach is required to take the playback system into consideration.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Informed TDoA-based Direction of Arrival Estimation for Hearing Aid Applications
- Log in to post comments
This presentation deals with estimation of the target sound Direction of Arrival (DoA) for a Hearing Aid System (HAS) which can connect to a wireless microphone worn by a target talker. In this setup, the HAS is "informed" about the almost noise-free content of the target sound via the wireless microphone and can use this information for the DoA estimation. Here, we propose an "informed" DoA estimator based on the Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) of the target sound at two microphones mounted on the ears of the HAS user---one microphone on each ear.
GlobalSIP.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Time-Shifting Based Primary-Ambient Extraction for Spatial Audio Reproduction
- Log in to post comments
One of the key issues in spatial audio analysis and reproduction is to decompose a signal into primary and ambient components based on their directional and diffuse spatial features, respectively. Existing approaches employed in primary-ambient extraction (PAE), such as principal component analysis (PCA), are mainly based on a basic stereo signal model. The performance of these PAE approaches has not been well studied for the input signals that do not satisfy all the assumptions of the stereo signal model.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Multi-shift principal component analysis based primary component extraction for spatial audio reproduction (poster)
- Log in to post comments
In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, one of the key issues is to decompose a signal into primary and ambient components based on their spatial features. Principal component analysis (PCA) has been widely employed in primary component extraction, and shifted PCA (SPCA) is employed to enhance the primary extraction for input signals involving the inter-channel time difference. However, SPCA generally requires the primary components to come from one direction and cannot produce good results in the case of multiple directions.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views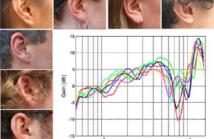
- Read more about On the Preprocessing and Postprocessing of HRTF individualization based on sparse representation of anthropometric features (poster)
- Log in to post comments
Individualization of head-related transfer functions (HRTFs) can be realized using the person’s anthropometry with a pre-trained model. This model usually establishes a direct linear or non-linear mapping from anthropometry to HRTFs in the training database. Due to the complex relation between anthropometry and HRTFs, the accuracy of this model depends heavily on the correct selection of the anthropometric features.
- Categories:
 182 Views
182 Views
- Read more about 3D Sound Effect Analysis, Synthesis and Application Design----A Primary-Ambient Extraction Approach (slides)
- Log in to post comments
In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, one of the key issues is to decompose a signal into primary and ambient components based on their spatial features. Stereo audio signals are often modeled as a linear mixture of primary and ambient components. Existing approaches like principal component analysis (PCA) and least squares (LS) have been widely employed to extract primary and ambient components from stereo signals. However, the performance and comparisons of these approaches in primary-ambient extraction (PAE) have not been well studied.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about 3D Sound Effect Analysis, Synthesis and Application Design----A Primary-Ambient Extraction Approach
- Log in to post comments
In spatial audio analysis-synthesis, one of the key issues is to decompose a signal into primary and ambient components based on their spatial features. Stereo audio signals are often modeled as a linear mixture of primary and ambient components. Existing approaches like principal component analysis (PCA) and least squares (LS) have been widely employed to extract primary and ambient components from stereo signals. However, the performance and comparisons of these approaches in primary-ambient extraction (PAE) have not been well studied.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views