
- Read more about Paper
- Log in to post comments
Clusters of neurons generate electrical signals which propagate in all directions through brain tissue, skull, and scalp of different conductivity. Measuring these signals with electroencephalography (EEG) sensors placed on the scalp results in noisy data. This can have severe impact on estimation, such as, source localization and temporal response functions (TRFs). We hypothesize that some of the noise is due to a Wiener-structured signal propagation with both linear and nonlinear components.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views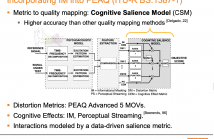
- Read more about An Improved Metric of Informational Masking for Perceptual Audio Quality Measurement
- Log in to post comments
Perceptual audio quality measurement systems algorithmically analyze the output of audio processing systems to estimate possible perceived quality degradation using perceptual models of human audition. In this manner, they save the time and resources associated with the design and execution of listening tests (LTs). Models of disturbance audibility predicting peripheral auditory masking in quality measurement systems have considerably increased subjective quality prediction performance of signals processed by perceptual audio codecs.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views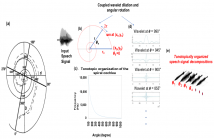
- Read more about Cochlear Decomposition: A Novel Bio-inspired Multiscale Analysis Framework
- Log in to post comments
Signal multiscale decomposition (SMD) is an effective analysis for
the identification of modal information in time-domain signals. So
far, various SMD approaches, such as the Multiresolution Wavelet
Transform (MWT), the Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD), and
the Variational Mode Decomosition (VMD) have been proposed,
However, issues, such as mode mixing for signals with closelyspaced
modes, have been identified. To confront such problems, we
propose here a novel spatial auditory decomposition framework for
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about Classifying Non-Individual Head-Related Transfer Functions with A Computational Auditory Model: Calibration And Metrics
- Log in to post comments
This study explores the use of a multi-feature Bayesian auditory sound localisation model to classify non-individual head-related transfer functions (HRTFs). Based on predicted sound localisation performance, these are grouped into ‘good’ and ‘bad’, and the ‘best’/‘worst’ is selected from each category. Firstly, we present a greedy algorithm for automated individual calibration of the model based on the individual sound localisation data.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
Despite there being clear evidence for attentional effects in biological spatial hearing, relatively few machine hearing systems exploit attention in binaural sound localisation. This paper addresses this issue by proposing a novel binaural machine hearing system with temporal attention for robust localisation of sound sources in noisy and reverberant conditions. A convolutional neural network is employed to extract noise-robust localisation features, which are similar to interaural phase difference, directly from phase spectra of the left and right ears for each frame.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about Image source method based on the directional impulse responses
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents the image source method for simulating the observed signals in the time-domain on the boundary of a spherical listening region. A wideband approach is used where all derivations are in the time-domain. The source emits a sequence of spherical wave fronts whose amplitudes could be related to the far-field directional impulse responses of a loudspeaker. Geometric methods are extensively used to model the observed signals. The spherical harmonic coefficients of the observed signals are also derived.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views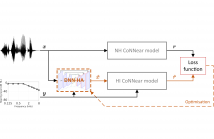
- Read more about DNN-HA: A DNN-based hearing-aid strategy for real-time processing
- Log in to post comments
Although hearing aids (HAs) can compensate for elevated hearing thresholds using sound amplification, they often fail to restore auditory perception in adverse listening conditions. Here, we present a deep-neural-network (DNN) HA processing strategy that can provide individualised sound processing for the audiogram of a listener using a single model architecture. Our multi-purpose HA model can be used for different individuals and can process audio inputs of 3.2 ms in <0.5 ms, thus paving the way for precise DNN-based treatments of hearing loss that can be embedded in hearing devices.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views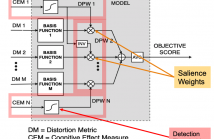
- Read more about A Data-Driven Cognitive Salience Model for Objective Perceptual Audio Quality Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Objective audio quality assessment systems often use perceptual models to predict the subjective quality scores of processed signals, as reported in listening tests. Most systems map different metrics of perceived degradation into a single quality score predicting subjective quality. This requires a quality mapping stage that is informed by real listening test data using statistical learning (\iec a data-driven approach) with distortion metrics as input features.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about CASCADED ALL-PASS FILTERS WITH RANDOMIZED CENTER FREQUENCIES AND PHASE POLARITY FOR ACOUSTIC AND SPEECH MEASUREMENT AND DATA AUGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
A new Time-Stretched-Pulse provides a solid foundation of acoustic measurements
Motivation: Measure and record speech data acquisition and presentation conditions
Issues: The target (real-world) systems consist of not only linear time-invariant but also non-linear time-invariant, random, and time-varying responses
Solution: We invented a simultaneous measurement of multiple paths by combining extended TSP signals with binary orthogonal weight sequences
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about CASCADED ALL-PASS FILTERS WITH RANDOMIZED CENTER FREQUENCIES AND PHASE POLARITY FOR ACOUSTIC AND SPEECH MEASUREMENT AND DATA AUGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
A new Time-Stretched-Pulse provides a solid foundation of acoustic measurements
Motivation: Measure and record speech data acquisition and presentation conditions
Issues: The target (real-world) systems consist of not only linear time-invariant but also non-linear time-invariant, random, and time-varying responses
Solution: We invented a simultaneous measurement of multiple paths by combining extended TSP signals with binary orthogonal weight sequences
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views