
This demo will showcase our video-to-audio model which attempts to reconstruct speech from short videos of spoken statements. Our model does so in a completely end-to-end manner where raw audio is generated based on the input video. This approach bypasses the need for separate lip-reading and text-to-speech models. The advantage of such an approach is that it does not require large transcribed datasets and it is not based on intermediate representations like text which remove any intonation and emotional content from the speech.
- Categories:
 105 Views
105 Views
- Read more about QUERY-BY-EXAMPLE SPOKEN TERM DETECTION USING ATTENTION-BASED MULTI-HOP NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about SEGMENTAL AUDIO WORD2VEC: REPRESENTING UTTERANCES AS SEQUENCES OF VECTORS WITH APPLICATIONS IN SPOKEN TERM DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about An LSTM-CTC based verification system for proxy-word based OOV keyword search
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about An LSTM-CTC based verification system for proxy-word based OOV keyword search
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views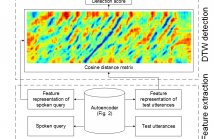
- Read more about Pairwise Learning using Multi-lingual Bottleneck Features for Low-resource Query-by-example Spoken Term Detection
- Log in to post comments
We propose to use a feature representation obtained by pairwise learning in a low-resource language for query-by-example spoken term detection (QbE-STD). We assume that word pairs identified by humans are available in the low-resource target language. The word pairs are parameterized by a multi-lingual bottleneck feature (BNF) extractor that is trained using transcribed data in high-resource languages. The multi-lingual BNFs of the word pairs are used as an initial feature representation to train an autoencoder (AE).
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views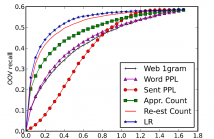
- Read more about Exploiting noisy web data by OOV ranking for low-resource keyword search
- Log in to post comments
Spoken keyword search in low-resource condition suffers from out-of-vocabulary (OOV) problem and insufficient text data for language model (LM) training. Web-crawled text data is used to expand vocabulary and to augment language model. However, the mismatching between web text and the target speech data brings difficulties to effective utilization. New words from web data need an evaluation to exclude noisy words or introduce proper probabilities. In this paper, several criteria to rank new words from web data are investigated and are used as features
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about KEYWORD SEARCH USING QUERY EXPANSION FOR GRAPH-BASED RESCORING OF HYPOTHESIZED DETECTIONS
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a novel framework for rescoring keyword search (KWS) detections using acoustic samples extracted from the training data. We view the keyword rescoring task as an information retrieval task and adopt the idea of query expansion. We expand a textual keyword with multiple speech keyword samples extracted from the training data. In this way, the hypothesized detections are compared with the multiple keywords using non-parametric approaches such as dynamic time warping (DTW).
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views