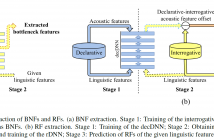
Speaking style plays an important role in the expressivity of speech for communication. Hence speaking style is very important for synthetic speech as well. Speaking style adaptation faces the difficulty that the data of specific styles may be limited and difficult to obtain in large amounts. A possible solution is to leverage data from speaking styles that are more available, to train the speech synthesizer and then adapt it to the target style for which the data is scarce.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about VOICE CONVERSION THROUGH RESIDUAL WARPING IN A SPARSE, ANCHOR-BASED REPRESENTATION OF SPEECH
- Log in to post comments
In previous work we presented a Sparse, Anchor-Based Representation of speech (SABR) that uses phonemic “anchors” to represent an utterance with a set of sparse non-negative weights. SABR is speaker-independent: combining weights from a source speaker with anchors from a target speaker can be used for voice conversion. Here, we present an extension of the original SABR that significantly improves voice conversion synthesis.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views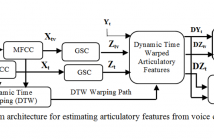
- Read more about QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF VOICE CONVERTED SPEECH USING ARTICULATORY FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel application of the acoustic- to- articulatory inversion (AAI) towards a quality assessment of the voice converted speech. The ability of humans to speak effortlessly requires the coordinated movements of various articulators, muscles, etc. This effortless movement contributes towards a naturalness, intelligibility and speaker’s identity (which is partially present in voice converted speech). Hence, during voice conversion (VC), the information related to the speech production is lost.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about NOVEL AMPLITUDE SCALING METHOD FOR BILINEAR FREQUENCY WARPING-BASED VOICE CONVERSION
- Log in to post comments
In frequency warping (FW)-based Voice Conversion (VC), the source spectrum is modified to match the frequency-axis of the target spectrum followed by an Amplitude Scaling (AS) to compensate the amplitude differences between the warped spectrum and the actual target spectrum. In this paper, we propose a novel AS technique which linearly transfers the amplitude of the frequency warped spectrum using the knowledge of a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM)-based converted spectrum without adding any spurious peaks.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views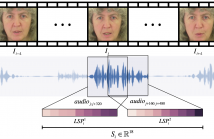
Speechreading is a notoriously difficult task for humans to perform. In this paper we present an end-to-end model based on a convolutional neural network (CNN) for generating an intelligible acoustic speech signal from silent video frames of a speaking person. The proposed CNN generates sound features for each frame based on its neighboring frames. Waveforms are then synthesized from the learned speech features to produce intelligible speech.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about Improvements on Punctuation Generation Inspired Linguistic Features for Mandarin Prosody Generation
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes two types of machine-extracted linguistic features from unlimited text input for Mandarin prosody generation. One is the improved punctuation confidence (iPC) which is a modified version of the previously proposed punctuation confidence that represents likelihood of inserting major punctuation marks (PMs) at word boundaries. Another is the quotation confidence (QC) which measures likelihood of a word string to be quoted as a meaningful or emphasized unit.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
This paper presents a deep neural network (DNN)-based unit selection method for waveform concatenation speech synthesis using frame-sized speech segments. In this method, three DNNs are adopted to calculate target costs and concatenation costs respectively for selecting frame-sized candidate units. The first DNN is built in the same way as the DNN-based statistical parametric speech synthesis, which predicts target acoustic features given linguistic context inputs.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Dictionary Update for NMF-based Voice Conversion Using an Encoder-Decoder Network
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a dictionary update method for Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (NMF) with high dimensional data in a spectral conversion (SC) task. Voice conversion has been widely studied due to its potential applications such as personalized speech synthesis and speech enhancement. Exemplar-based NMF (ENMF) emerges as an effective and probably the simplest choice among all techniques for SC, as long as a source-target parallel speech corpus is given. ENMF-based SC systems usually need a large amount of bases (exemplars) to ensure the quality of the converted speech.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Tongue Shape Variation Model for Simulating Mandarin Chinese Articulation
- Log in to post comments
We studied tongue shapes extracted from X-ray films which were taken during the process of mandarin Chinese articulation. Through factor analysis, we built an eight-parameter-driven tongue articulation model. This study reveals that the front of the tongue has large horizontal movement; the blade of the tongue has large vertical movement; whereas the back, as well as the root, of the tongue has small movement both horizontally and vertically. This model can be used to drive a 3D tongue model to control its articulatory behavior.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views- Read more about A SPEAKER ADAPTATION TECHNIQUE FOR GAUSSIAN PROCESS REGRESSION BASED SPEECH SYNTHESIS USING FEATURE SPACE TRANSFORM
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views