
- Read more about Transformer-based text-to-speech with weighted forced attention
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates state-of-the-art Transformer- and FastSpeech-based high-fidelity neural text-to-speech (TTS) with full-context label input for pitch accent languages. The aim is to realize faster training than conventional Tacotron-based models. Introducing phoneme durations into Tacotron-based TTS models improves both synthesis quality and stability.
- Categories:
 290 Views
290 Views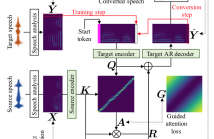
- Read more about AttS2S-VC: Sequence-to-Sequence Voice Conversion with Attention and Context Preservation Mechanisms
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes a method based on a sequence-to-sequence learning (Seq2Seq) with attention and context preservation mechanism for voice conversion (VC) tasks. Seq2Seq has been outstanding at numerous tasks involving sequence modeling such as speech synthesis and recognition, machine translation, and image captioning.
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views
- Read more about An End-to-End Network to Synthesize Intonation using a Generalized Command Response Model - Poster
- Log in to post comments
The generalized command response (GCR) model represents intonation as a
superposition of muscle responses to spike command signals. We have previously
shown that the spikes can be predicted by a two-stage system, consisting of a recurrent neural network and a post-processing procedure, but the responses themselves were fixed dictionary atoms. We propose an end-to-end
neural architecture that replaces the dictionary atoms with trainable
second-order recurrent elements analogous to recursive filters. We demonstrate
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Views
- Read more about Investigations of real-time Gaussian FFTNet and parallel WaveNet neural vocoders with simple acoustic features
- Log in to post comments
This paper examines four approaches to improving real-time neural vocoders with simple acoustic features (SAF) constructed from fundamental frequency and mel-cepstra rather than mel-spectrograms.
- Categories:
 350 Views
350 Views
- Read more about CycleGAN-VC2: Improved CycleGAN-based Non-parallel Voice Conversion
- Log in to post comments
Non-parallel voice conversion (VC) is a technique for learning the mapping from source to target speech without relying on parallel data. This is an important task, but it has been challenging due to the disadvantages of the training conditions. Recently, CycleGAN-VC has provided a breakthrough and performed comparably to a parallel VC method without relying on any extra data, modules, or time alignment procedures. However, there is still a large gap between the real target and converted speech, and bridging this gap remains a challenge.
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views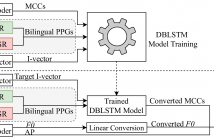
- Read more about CROSS-LINGUAL VOICE CONVERSION WITH BILINGUAL PHONETIC POSTERIORGRAM AND AVERAGE MODELING
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a cross-lingual voice conversion approach using bilingual Phonetic PosteriorGram (PPG) and average modeling. The proposed approach makes use of bilingual PPGs to represent speaker-independent features of speech signals from different languages in the same feature space. In particular, a bilingual PPG is formed by stacking two monolingual PPG vectors, which are extracted from two monolingual speech recognition systems. The conversion model is trained to learn the relationship between bilingual PPGs and the corresponding acoustic features.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views
- Read more about POSTER OF PAPER 3809 (SLP-P20)
- Log in to post comments
Poster presented at the poster session "Speech Synthesis II" of ICASSP 2019 of the paper "ENHANCED VIRTUAL SINGERS GENERATION BY INCORPORATING SINGING DYNAMICS TO PERSONALIZED TEXT-to-SPEECH-to-SINGING"
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views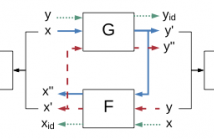
- Read more about Cycle-consistent adversarial networks for non-parallel vocal effort based speaking style conversion
- Log in to post comments
Speaking style conversion (SSC) is the technology of converting natural speech signals from one style to another. In this study, we propose the use of cycle-consistent adversarial networks (CycleGANs) for converting styles with varying vocal effort, and focus on conversion between normal and Lombard styles as a case study of this problem. We propose a parametric approach that uses the Pulse Model in Log domain (PML) vocoder to extract speech features. These features are mapped using the CycleGAN from utterances in the source style to the corresponding features of target speech.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about DNN-BASED SPEAKER-ADAPTIVE POSTFILTERING WITH LIMITED ADAPTATION DATA FOR STATISTICAL SPEECH SYNTHESIS SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have been successfully deployed for acoustic modelling in statistical parametric speech synthesis (SPSS) systems. Moreover, DNN-based postfilters (PF) have also been shown to outperform conventional postfilters that are widely used in SPSS systems for increasing the quality of synthesized speech. However, existing DNN-based postfilters are trained with speaker-dependent databases. Given that SPSS systems can rapidly adapt to new speakers from generic models, there is a need for DNN-based postfilters that can adapt to new speakers with minimal adaptation data.
- Categories:
 138 Views
138 Views
- Read more about HIGH-QUALITY NONPARALLEL VOICE CONVERSION BASED ON CYCLE-CONSISTENT ADVERSARIAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views