
- Read more about SYNTHESIZING DYSARTHRIC SPEECH USING MULTI-SPEAKER TTS FOR DYSARTHRIC SPEECH RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about DRVC: A Framework of Any-to-Any Voice Conversion with Self-Supervised Learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about ROBUST DISENTANGLED VARIATIONAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING FOR ZERO-SHOT VOICE CONVERSION
- Log in to post comments
Traditional studies on voice conversion (VC) have made progress with parallel training data and known speakers. Good voice conversion quality is obtained by exploring better alignment modules or expressive mapping functions. In this study, we investigate zero-shot VC from a novel perspective of self-supervised disentangled speech representation learning. Specifically, we achieve the disentanglement by balancing the information flow between global speaker representation and time-varying content representation in a sequential variational autoencoder (VAE).
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Word-level Prosody Tagging for Controllable Speech Synthesis
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Recurrent Phase Reconstruction Using Estimated Phase Derivatives from Deep Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a deep neural network (DNN)-based system for phase reconstruction of speech signals solely from their magnitude spectrograms. The phase is very sensitive to time shifts. Therefore it is meaningful to estimate the phase derivatives instead of the phase directly, e.g., using DNNs and then apply a phase reconstruction method to recombine these estimates to a suitable phase spectrum. In this paper, we propose three changes for such a two-stage phase reconstruction system.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Recurrent Phase Reconstruction Using Estimated Phase Derivatives from Deep Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a deep neural network (DNN)-based system for phase reconstruction of speech signals solely from their magnitude spectrograms. The phase is very sensitive to time shifts. Therefore it is meaningful to estimate the phase derivatives instead of the phase directly, e.g., using DNNs and then apply a phase reconstruction method to recombine these estimates to a suitable phase spectrum. In this paper, we propose three changes for such a two-stage phase reconstruction system.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about MaskCycleGAN-VC: Learning Non-parallel Voice Conversion with Filling in Frames
- Log in to post comments
This work is concerned with non-parallel voice conversion. In particular, motivated by the recent advances in mel-spectrogram-based vocoders, we focus on conversions in the mel-spectrogram domain based on CycleGAN. The challenge is how to make the converter able to convert only the voice factors while retaining the linguistic content factors that underlie input mel-spectrograms. To solve this, we propose MaskCycleGAN-VC, which is an extension of CycleGAN-VC2 and is trained using a novel auxiliary task called filling in frames (FIF). With FIF, we apply a temporal mask to the input mel-spectrogram and encourage the converter to fill in missing frames based on surrounding frames. This task allows the converter to learn time-frequency structures in a self-supervised manner. A subjective evaluation of the naturalness and speaker similarity showed that MaskCycleGAN-VC outperformed previous CycleGAN-VCs.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about NON-PARALLEL MANY-TO-MANY VOICE CONVERSION BY KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER FROM A TEXT-TO-SPEECH MODEL
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Context-Aware Prosody Correction for Text-Based Speech Editing
- Log in to post comments
Text-based speech editors expedite the process of editing speech recordings by permitting editing via intuitive cut, copy, and paste operations on a speech transcript. A major drawback of current systems, however, is that edited recordings often sound unnatural because of prosody mismatches around edited regions. In our work, we propose a new context-aware method for more natural sounding text-based editing of speech.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views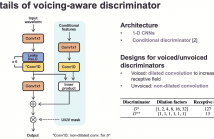
- Read more about Parallel waveform synthesis based on generative adversarial networks with voicing-aware conditional discriminators
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes voicing-aware conditional discriminators for Parallel WaveGAN-based waveform synthesis systems. In this framework, we adopt a projection-based conditioning method that can significantly improve the discriminator's performance. Furthermore, the conventional discriminator is separated into two waveform discriminators for modeling voiced and unvoiced speech.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views