
The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about FACE ANTI-SPOOFING VIA DEEP LOCAL BINARY PATTERNS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views- Read more about MULTI-VIEW VISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION BASED ON MULTI TASK LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
Visual speech recognition (VSR), also known as lip reading is a task that recognizes words or phrases using video clips of lip movement. Traditional VSR methods are limited in that they are based mostly on VSR of frontal-view facial movement. However, for practical application, VSR should include lip movement from all angles. In this paper, we propose a pose-invariant network which can recognize words spoken from any arbitrary view input.
- Categories:
 142 Views
142 Views- Read more about COUPLED ANALYSIS-SYNTHESIS DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel coupled dictionary learning method, namely coupled analysis-synthesis dictionary learning, to improve the performance of person re-identification in the non-overlapping fields of different camera views. Most of the existing coupled dictionary learning methods train a coupled synthesis dictionary directly on the original feature spaces, which limits the representation ability of the dictionary.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views- Read more about LONG-TERM OBJECT TRACKING BASED ON SIAMESE NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about ICIP2017_Incremental zero-shot learning based on attributes for image classification
- Log in to post comments
Instead of assuming a closed-world environment comprising a fixed number of objects, modern pattern recognition systems need to recognize outliers, identify anomalies, or discover entirely new objects, which is known as zero-shot object recognition. However, many existing zero-shot learning methods are not efficient enough to incrementally update themselves with new samples mixed with known or novel class labels. In this paper, we propose an incremental zero-shot learning framework (IIAP/QR) based on indirect-attribute-prediction (IAP) model. Firstly, a fast incremental
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views- Read more about ICIP 2017-ROBUST ELLIPSE DETECTION VIA ARC SEGMENTATION AND CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views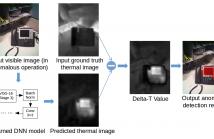
- Read more about Anomaly Detection in Thermal Images Using Deep Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
icip_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 156 Views
156 Views- Read more about MODELING STRUCTURAL DISSIMILARITY BASED ON SHAPE EMBODIMENT FOR CELL SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Accurate cell segmentation is one of the critical, yet challenging problems in microscopy images due to ambiguous boundaries as well as a wide variation of shapes and sizes of cells. Even though a number of existing methods have achieved decent results for cell segmentation, boundary vagueness between adjoining cells tended to cause generation of perceptually inaccurate segmentation of stained nuclei. We propose
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views- Read more about ICIP 2017 Poster Paper 3060
- Log in to post comments
Top-down attention plays an important role in guidance of human attention in real-world scenarios, but less efforts in computational modeling of visual attention has been put on it. Inspired by the mechanisms of top-down attention in human visual perception, we propose a multi-layer linear model of top-down attention to modulate bottom-up saliency maps actively. The first layer is a linear regression model which combines the bottom-up saliency maps on various visual features and objects.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Street-to-Shop Shoe Retrieval with Multi-Scale Viewpoint Invariant Triplet Network
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we aim to find exactly the same shoes given a daily shoe photo (street scenario) that matches the online shop shoe photo (shop scenario). There are large visual differences between the street and shop scenario shoe images. To handle the discrepancy of different scenarios, we learn a feature embedding for shoes via a viewpoint-invariant triplet network, the feature activations of which reflect the inherent similarity between any two shoe images.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views