
- Read more about Time Difference of Arrival Estimation from Frequency-sliding Generalized Cross-Correlations Using Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
The interest in deep learning methods for solving traditional signal processing tasks has been steadily growing in the last years.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views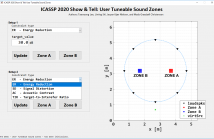
- Read more about User Tuneable Sound Zones
- Log in to post comments
Creating sound zones has been an active area of research since it was first introduced. Generally, this can be done either by maximizing an acoustic contrast that represents the acoustic potential energy ratio between the bright and dark zones or by minimizing a reproduction error between the desired and reproduced sound fields. However, the former suffers from severe distortion in the reproduced sound field, whereas the latter suffers from poor acoustic contrast.
- Categories:
 70 Views
70 Views
- Read more about RAW WAVEFORM BASED END-TO-END DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORK FOR SPATIAL LOCALIZATION OF MULTIPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCES
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present an end-to-end deep convolutional neural network operating on multi-channel raw audio data to localize multiple simultaneously active acoustic sources in space. Previously reported end-to-end deep learning based approaches work well in localizing a single source directly from multi-channel raw-audio, but are not easily extendable to localize multiple sources due to the well known permutation problem.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views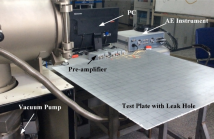
- Read more about LEAK DETECTION OF SPACECRAFT IN ORBIT USING ULTRASONIC SENSOR ARRAY BY LAMB WAVES
- Log in to post comments
With the increasing of human space activities, the number of space debris has increased dramatically, the possibility that spacecraft in orbit is impacted by space debris is growing. It is important to detect and locate the gas leak accurately and timely. In this paper, a leak detection method using ultrasonic sensor array is proposed. Firstly, the ultrasonic sensor array is used to detect the leak acoustic signal which propagates as Lamb wave through spacecraft structure. Then we apply beam forming algorithm to determine the direction of the leak source.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Performance Bounds for Displaced Sensor Automotive Radar Imaging
- Log in to post comments
In automotive radar imaging, displaced sensors offer improvement in localization accuracy by jointly processing the data acquired from multiple radar units, each of which may have limited individual resources. In this paper, we derive performance bounds on the estimation error of target parameters processed by displaced sensors that correspond to several independent radars mounted at different locations on the same vehicle. Unlike previous studies, we do not assume a very accurate time synchronization among the sensors.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Simplified 2D mmWave Near-Field Imaging
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
In this tutorial, simplified signal processing techniques for near-field 2-D image formation is introduced and the specifications of the recorded SAR data samples are detailed.
The source code and example data set can be accessed via the following links:
- Categories:
 248 Views
248 Views
- Read more about 3-D MIMO-SAR Imaging Using Multi-Chip Cascaded Millimeter-Wave Sensors
- Log in to post comments
Integration of multi-chip cascaded multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) millimeter-wave (mmWave) sensors with synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging will enable cost-effective and scalable solutions for a variety of applications including security, automotive, and surveillance. In this paper, the first three-dimensional (3-D) holographic MIMO-SAR imaging system using cascaded mmWave sensors is designed and implemented. The challenges imposed by the use of cascaded mmWave sensors in high-resolution MIMO-SAR imaging systems are discussed.
- Categories:
 522 Views
522 Views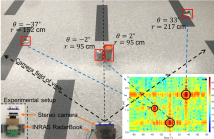
- Read more about Exploiting Structural Information in Camera Aided Radar Parameter Estimation
- Log in to post comments
The sparse nature of the ranging and spatial angle
parameter space has been exploited by many radar parameter
estimation algorithms in literature. We note that real world
reflections are not sporadically sparse in the parameter space and
typically exhibit smooth variation effects with non-zero entries
occurring in clusters. In this paper, we explicitly model this
additional structural information into our estimation algorithm
and propose a non-convex regularization of the linear observation
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about Compressive Super-Pixel LiDAR for High-Framerate 3D Depth Imaging
- Log in to post comments
We propose a new sampling and reconstruction framework for full frame depth imaging using synchronised, programmable laser diode and photon detector arrays. By adopting a measurement scheme that probes the environment with sparse, pseudo-random patterns, our method enables eyesafe LiDAR operation, while guaranteeing fast reconstruction of
- Categories:
 222 Views
222 Views
- Read more about KPSNET: KEYPOINT DETECTION AND FEATURE EXTRACTION FOR POINT CLOUD REGISTRATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents the KPSNet, a KeyPoint Siamese Network to simultaneously learn task-desirable keypoint detector and feature extractor. The keypoint detector is optimized to predict a score vector, which signifies the probability of each candidate being a keypoint. The feature extractor is optimized to learn robust features of keypoints by exploiting the correspondence between the keypoints generated from two inputs, respectively. For training, the KPSNet does not require to manually annotate keypoints and local patches pairwise.
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views