- Read more about 'TEXCEPTION: A Character/Word-Level Deep Learning Model for Phishing URL Detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 188 Views
188 Views
- Read more about SQUAREMIX: A Faster Pseudorandom Number Generator for Dynamic-Multithreading Platforms
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about END-TO-END PERSON SEARCH SEQUENTIALLY TRAINED ON AGGREGATED DATASET
- Log in to post comments
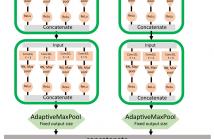
In video surveillance applications, person search is a chal-
lenging task consisting in detecting people and extracting
features from their silhouette for re-identification (re-ID) pur-
pose. We propose a new end-to-end model that jointly com-
putes detection and feature extraction steps through a single
deep Convolutional Neural Network architecture. Sharing
feature maps between the two tasks for jointly describing
people commonalities and specificities allows faster runtime,
which is valuable in real-world applications. In addition
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views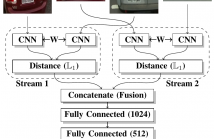
- Read more about A TWO-STREAM SIAMESE NEURAL NETWORK FOR VEHICLE RE-IDENTIFICATION BY USING NON-OVERLAPPING CAMERAS
- Log in to post comments
We describe in this paper a Two-Stream Siamese Neural Network for vehicle re-identification. The proposed network is fed simultaneously with small coarse patches of the vehicle shape’s, with 96 × 96 pixels, in one stream, and fine features extracted from license plate patches, easily readable by humans, with 96 × 48 pixels, in the other one.
ICIP 2019.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Efficient Person Re-Identification in Videos Using Sequence Lazy Greedy Determinantal Point Process (SLGDPP)
- Log in to post comments
Given a sequence of observations for each person in each camera, identifying or re-identifying the same person across different cameras is one of the objectives of video surveillance systems. In the case of video based person re-id, the challenge is to handle the high correlation between temporally adjacent frames. The presence of non-informative frames results in high redundancy which needs to be removed for an efficient re-id.
- Categories:
 105 Views
105 Views
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views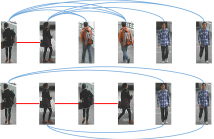
- Read more about Deep Feature Embedding Learning for Person Re-Identification Using Lifted Structured Loss
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose deep feature embedding learning for person re-identification (re-id) using lifted structured loss. Although triplet loss has been commonly used in deep neural networks for person re-id, the triplet loss-based framework is not effective in fully using the batch information. Thus, it needs to choose hard negative samples manually that is very time-consuming. To address this problem, we adopt lifted structured loss for deep neural networks that makes the network learn better feature embedding by minimizing intra-class variation and maximizing inter-class variation.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about Trade-offs in Data-Driven False Data Injection Attacks Against the Power Grid
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of constructing false data injection (FDI) attacks that can bypass the bad data detector (BDD) of a power grid. The attacker is assumed to have access to only power flow measurement data traces (collected over a limited period of time) and no other prior knowledge about the grid. Existing related algorithms are formulated under the assumption that the attacker has access to measurements collected over a long (asymptotically infinite) time period, which may not be realistic.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about TIC-TAC, FORGERY TIME HAS RUN-UP! LIVE ACOUSTIC WATERMARKING FOR INTEGRITY CHECK IN FORENSIC APPLICATIONS
- Log in to post comments
A common problem in audio forensics is the difficulty to
authenticate an audio recording. In this paper we provide a novel
and reliable solution to this problem by making use of a control
signal, visible and audible on the actual recording, yet ignored by
the listener, the TIC-TAC signal. We describe our live watermark
solution, we incorporate it in an integrity check algorithm and we
provide meaningful preliminary tests. Their results, computed in
terms of precision show an outstanding performance: 100%
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views