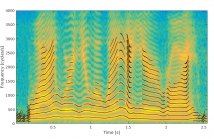
- Read more about Optimizing Short-Time Fourier Transform Parameters via Gradient Descent
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views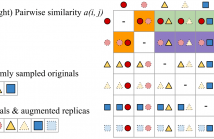
- Read more about Neural Audio Fingerprint for High-specific Audio Retrieval based on Contrastive Learning
- Log in to post comments
Most of existing audio fingerprinting systems have limitations to be used for high-specific audio retrieval at scale. In this work, we generate a low-dimensional representation from a short unit segment of audio, and couple this fingerprint with a fast maximum inner-product search. To this end, we present a contrastive learning framework that derives from the segment-level search objective. Each update in training uses a batch consisting of a set of pseudo labels, randomly selected original samples, and their augmented replicas.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Seen and Unseen emotional style transfer for voice conversion with a new emotional speech dataset
- Log in to post comments
Emotional voice conversion aims to transform emotional prosody in speech while preserving the linguistic content and speaker identity. Prior studies show that it is possible to disentangle emotional prosody using an encoder-decoder network conditioned on discrete representation, such as one-hot emotion labels. Such networks learn to remember a fixed set of emotional styles.
icassp_poster.pdf
icassp_slides.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about DENOISPEECH: DENOISING TEXT TO SPEECH WITH FRAME-LEVEL NOISE MODELING
- Log in to post comments
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views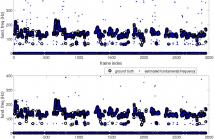
Most parametric fundamental frequency estimators make the implicit assumption that any corrupting noise is additive, white Gaussian. Under this assumption, the maximum likelihood (ML) and the least squares estimators are the same, and statistically efficient. However, in the coloured noise case, the estimators differ, and the spectral shape of the corrupting noise should be taken into account.
- Categories:
 165 Views
165 Views- Read more about VaPar Synth - A Variational Parametric Model for Audio Synthesis
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
With the advent of data-driven statistical modeling and abundant computing power, researchers are turning increasingly to deep learning for audio synthesis. These methods try to model audio signals directly in the time or frequency domain. In the interest of more flexible control over the generated sound, it could be more useful to work with a parametric representation of the signal which corresponds more directly to the musical attributes such as pitch, dynamics and timbre.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about AMA: An Open-source Amplitude Modulation Analysis Toolkit for Signal Processing Applications
- Log in to post comments
For their analysis with conventional signal processing tools, non-stationary signals are assumed to be stationary (or at least wide-sense stationary) in short intervals. While this approach allows them to be studied, it disregards the temporal evolution of their statistics. As such, to analyze this type of signals, it is desirable to use a representation that registers and characterizes the temporal changes in the frequency content of the signals, as these changes may occur in single or multiple periodic ways.
globalsip_2019.pdf
- Categories:
 126 Views
126 Views
- Read more about DNN-BASED SPEAKER-ADAPTIVE POSTFILTERING WITH LIMITED ADAPTATION DATA FOR STATISTICAL SPEECH SYNTHESIS SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have been successfully deployed for acoustic modelling in statistical parametric speech synthesis (SPSS) systems. Moreover, DNN-based postfilters (PF) have also been shown to outperform conventional postfilters that are widely used in SPSS systems for increasing the quality of synthesized speech. However, existing DNN-based postfilters are trained with speaker-dependent databases. Given that SPSS systems can rapidly adapt to new speakers from generic models, there is a need for DNN-based postfilters that can adapt to new speakers with minimal adaptation data.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about F0 CONTOUR ESTIMATION USING PHONETIC FEATURE IN ELECTROLARYNGEAL SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
Pitch plays a significant role in understanding a tone based language like Mandarin. In this paper, we present a new method that estimates F0 contour for electrolaryngeal (EL) speech enhancement in Mandarin. Our system explores the usage of phonetic feature to improve the quality of EL speech. First, we train an acoustic model for EL speech and generate the phoneme posterior probabilities feature sequence for each input EL speech utterance. Then we employ the phonetic feature for F0 contour generation rather than the acoustic feature.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views