- Read more about UNIT-DSR: DYSARTHRIC SPEECH RECONSTRUCTION SYSTEM USING SPEECH UNIT NORMALIZATION
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
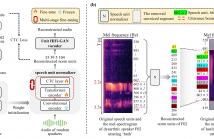
Dysarthric speech reconstruction (DSR) systems aim to automatically convert dysarthric speech into normal-sounding speech. The technology eases communication with speakers affected by the neuromotor disorder and enhances their social inclusion.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views
- Read more about Adaptive speech emotion representation learning based on dynamic graph
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Graph representation learning has become a hot research topic due to its powerful nonlinear fitting capability in extracting representative node embeddings. However, for sequential data such as speech signals, most traditional methods merely focus on the static graph created within a sequence, and largely overlook the intrinsic evolving patterns of these data. This may reduce the efficiency of graph representation learning for sequential data.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about Multi-Level Graph Learning For Audio Event Classification And Human-Perceived Annoyance Rating Prediction
- Log in to post comments
WHO's report on environmental noise estimates that 22 M people suffer from chronic annoyance related to noise caused by audio events (AEs) from various sources. Annoyance may lead to health issues and adverse effects on metabolic and cognitive systems. In cities, monitoring noise levels does not provide insights into noticeable AEs, let alone their relations to annoyance. To create annoyance-related monitoring, this paper proposes a graph-based model to identify AEs in a soundscape, and explore relations between diverse AEs and human-perceived annoyance rating (AR).
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about GCT: GATED CONTEXTUAL TRANSFORMER FOR SEQUENTIAL AUDIO TAGGING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Self-supervised learning of audio representations using angular contrastive loss
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Audio-Caption Aligning Learns Correspondences between Individual Sound Events and Textual Phrases
- Log in to post comments
We investigate unsupervised learning of correspondences between sound events and textual phrases through aligning audio clips with textual captions describing the content of a whole audio clip. We align originally unaligned and unannotated audio clips and their captions by scoring the similarities between audio frames and words, as encoded by modality-specific encoders and using a ranking-loss criterion to optimize the model.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Generalizing AUC Optimization to Multiclass Classification for Audio Segmentation With Limited Training Data
- Log in to post comments
Area under the ROC curve (AUC) optimisation techniques developed for neural networks have recently demonstrated their capabilities in different audio and speech related tasks. However, due to its intrinsic nature, AUC optimisation has focused only on binary tasks so far. In this paper, we introduce an extension to the AUC optimisation framework so that it can be easily applied to an arbitrary number of classes, aiming to overcome the issues derived from training data limitations in deep learning solutions.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views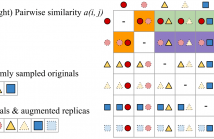
- Read more about Neural Audio Fingerprint for High-specific Audio Retrieval based on Contrastive Learning
- Log in to post comments
Most of existing audio fingerprinting systems have limitations to be used for high-specific audio retrieval at scale. In this work, we generate a low-dimensional representation from a short unit segment of audio, and couple this fingerprint with a fast maximum inner-product search. To this end, we present a contrastive learning framework that derives from the segment-level search objective. Each update in training uses a batch consisting of a set of pseudo labels, randomly selected original samples, and their augmented replicas.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views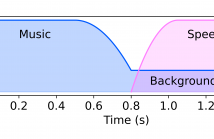
- Read more about ARTIFICIALLY SYNTHESISING DATA FOR AUDIO CLASSIFICATION AND SEGMENTATION TO IMPROVE SPEECH AND MUSIC DETECTION IN RADIO BROADCAST
- Log in to post comments
Segmenting audio into homogeneous sections such as music and speech helps us understand the content of audio. It is useful as a pre-processing step to index, store, and modify audio recordings, radio broadcasts and TV programmes. Deep learning models for segmentation are generally trained on copyrighted material, which cannot be shared. Annotating these datasets is time-consuming and expensive and therefore, it significantly slows down research progress. In this study, we present a novel procedure that artificially synthesises data that resembles radio signals.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views