
- Read more about Investigating the Effect of Sound-Event Loudness on Crowdsourced Audio Annotations
- Log in to post comments
Audio annotation is an important step in developing machine-listening systems. It is also a time consuming process, which has motivated investigators to crowdsource audio annotations. However, there are many factors that affect annotations, many of which have not been adequately investigated. In previous work, we investigated the effects of visualization aids and sound scene complexity on the quality of crowdsourced sound-event annotations.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about SAMPLERNN-BASED NEURAL VOCODER FOR STATISTICAL PARAMETRIC SPEECH SYNTHESIS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a SampleRNN-based neural vocoder for statistical parametric speech synthesis. This method utilizes a conditional SampleRNN model composed of a hierarchical structure of GRU layers and feed-forward layers to capture long-span dependencies between acoustic features and waveform sequences. Compared with conventional vocoders based on the source-filter model, our proposed vocoder is trained without assumptions derived from the prior knowledge of speech production and is able to provide a better modeling and recovery of phase information.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about SAMPLERNN-BASED NEURAL VOCODER FOR STATISTICAL PARAMETRIC SPEECH SYNTHESIS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a SampleRNN-based neural vocoder for statistical parametric speech synthesis. This method utilizes a conditional SampleRNN model composed of a hierarchical structure of GRU layers and feed-forward layers to capture long-span dependencies between acoustic features and waveform sequences. Compared with conventional vocoders based on the source-filter model, our proposed vocoder is trained without assumptions derived from the prior knowledge of speech production and is able to provide a better modeling and recovery of phase information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views- Read more about REVISITING THE PROBLEM OF AUDIO-BASED HIT SONG PREDICTION USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Being able to predict whether a song can be a hit has important applications in the music industry. Although it is true that the popularity of a song can be greatly affected by external factors such as social and commercial influences, to which degree audio features computed from musical signals (whom we regard as internal factors) can predict song popularity is an interesting research question on its own.
icassp2017.pdf
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views- Read more about Global Variance in Speech Synthesis with Linear Dynamical Models
- Log in to post comments
GV_LDM.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about poster_STEGANALYSIS OF AAC USINGCALIBRATED MARKOV MODEL OF ADJACENT CODEBOOK
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about poster_STEGANALYSIS OF AAC USINGCALIBRATED MARKOV MODEL OF ADJACENT CODEBOOK
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about Lecture ICASSP 2016 Pierre Laffitte
- Log in to post comments
This presentation introduces a Deep Learning model that performs classification of the Audio Scene in the subway environment. The final goal is to detect Screams and Shouts for surveillance purposes. The model is a combination of Deep Belief Network and Deep Neural Network, (generatively pre-trained within the DBN framework and fine-tuned discriminatively within the DNN framework), and is trained on a novel database of pseudo-real signals collected in the Paris metro.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views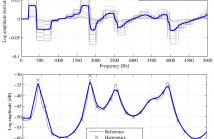
- Read more about A Time Regularization Technique for Discrete Spectral Envelopes Through Frequency Derivative
- Log in to post comments
Abstract—In most applications of sinusoidal models for speech
signal, an amplitude spectral envelope is necessary. This envelope
is not only assumed to fit the vocal tract filter response as
accurately as possible, but it should also exhibit slow varying
shapes across time. Indeed, time irregularities can generate
artifacts in signal manipulations or increase improperly the
features variance used in statistical models. In this letter, a
simple technique is suggested to improve this time regularity.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views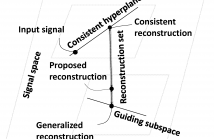
- Read more about Guided Signal Reconstruction with Application to Image Magnification
- Log in to post comments
We propose signal reconstruction algorithms which utilize a guiding subspace that represents desired properties of reconstructed signals. Optimal reconstructed signals are shown to belong to a convex bounded set, called the ``reconstruction'' set. Iterative reconstruction algorithms, based on conjugate gradient methods, are developed to approximate optimal reconstructions with low memory and computational costs. Effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated with an application to image magnification.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views