- Read more about Probabilistic Analysis of Tone Reservation Method for the PAPR Reduction of OFDM Systems
- Log in to post comments
High peak values of transmission signals in wireless communication systems lead to wasteful energy consumption and degradation of several transmission performances. We continue the theoretical contributions made by Boche and Farell towards the understanding of peak value reduction, using the strategy known as tone reservation for orthogonal transmission schemes. There it was shown that for OFDM systems, the combinatorial object called arithmetic progression plays an important role in setting limitations for the applicability of the tone reservation method.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Decentralized Sparsity Pattern Recovery using 1-bit Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of decentralized joint sparsity pattern recovery based on 1-bit compressive measurements in a distributed network. We assume that the distributed nodes observe sparse signals which share the same but unknown sparsity pattern. Each node obtains measurements via random projections and further quantizes
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about A STUDY ON MIXING SEQUENCES IN MODULATED WIDEBAND CONVERTERS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we study mixing sequences of modulated wideband converters (MWC). The MWC is a sub-Nyquist sampling system which mixes an input analog signal by multiple numbers of fast mixing sequences in parallel. When the mixing sequences are random cyclic shifts of a base sequence for a memory efficiency, the system turns into random partial Fourier structured MWC (RPFMWC). In RPFMWC, the spectrum distribution of a base sequence is important in reconstruction of the input signal.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 ViewsTo meet the ever-growing mobile data traffic, network spatial densification
with various low-power nodes in addition to the conventional high-power macro base
stations (BS), a.k.a. heterogeneous network (HetNet), is regarded as one key
enabling solution. Due to the unplanned nature, HetNets are very irregular and
severe interference can happen without judicious designs of the user association
rules. Conventional maximum downlink (DL) signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
(SINR) association rule, on the other hand, can not fully release the traffic
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views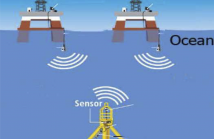
- Read more about RSS-BASED SENSOR LOCALIZATION IN UNDERWATER ACOUSTIC SENSOR NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Since the global positioning system (GPS) is not applicable underwater, source localization using wireless sensor networks (WSNs) is gaining popularity in oceanographic applications. Unlike terrestrial WSNs (TWSNs) which use electromagnetic signaling, underwater WSNs (UWSNs) require underwater acoustic (UWA) signaling. Received signal strength (RSS)-based source localization is considered in this paper due to its practical simplicity and the constraint of low-cost sensor devices, but this area received little attention so far because of the complicated UWA transmission loss (TL) phenomena.
RSSmain.pdf
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views- Read more about Opportunistic Spectrum Access with Temporal-Spatial Reuse in Cognitive Radio Networks
- Log in to post comments
We formulate and study a multi-user multi-armed bandit (MAB) problem that exploits the temporal-spatial reuse of primary user (PU) channels so that secondary users (SUs) who do not interfere with each other can make use of the same PU channel. We first propose a centralized channel allocation policy that has logarithmic regret, but requires a central processor to solve a NP-complete optimization problem at exponentially increasing time intervals.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views- Read more about MUTUAL INFORMATION BASED RADAR WAVEFORM DESIGN FOR JOINT RADAR AND CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views- Read more about Physical modeling and performance bounds for device-free localization systems
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about A DYNAMIC BAYESIAN NETWORK APPROACH FOR DEVICE-FREE RADIO VISION: MODELING, LEARNING AND INFERENCE FOR BODY MOTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Directional Maximum Likelihood Self-Estimation of the Path-Loss Exponent
- Log in to post comments
The path-loss exponent (PLE) is a key parameter in wireless propagation channels. Therefore, obtaining the knowledge of the PLE is rather significant for assisting wireless communications and networking to achieve a better performance. Most existing methods for estimating the PLE not only require nodes with known locations but also assume an omni-directional PLE. However, the location information might be unavailable or unreliable and, in practice, the PLE might change with the direction.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views