
- Read more about A RETINA-INSPIRED ENCODER: AN INNOVATIVE STEP ON IMAGE CODING USING LEAKY INTEGRATE-AND-FIRE NEURONS
- Log in to post comments
ICIP_2018.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about A Machine Learning Approach to Accurate Sequence-Level Rate Control Scheme for Video Coding
- Log in to post comments
Machine learning for CRF-Rate modeling in transcoding
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about SYMMETRY-BASED GRAPH FOURIER TRANSFORMS FOR IMAGE REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
It is well-known that the application of the Discrete Cosine Transform
(DCT) in transform coding schemes is justified by the fact that
it belongs to a family of transforms asymptotically equivalent to the
Karhunen-Loève Transform (KLT) of a first order Markov process.
However, when the pixel-to-pixel correlation is low the DCT does
not provide a compression performance comparable with the KLT.
In this paper, we propose a set of symmetry-based Graph Fourier
Transforms (GFT) whose associated graphs present a totally or partially
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views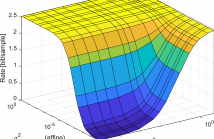
- Read more about Rate-Distortion Theory for Affine Global Motion Compensation in Video Coding
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we derive the rate-distortion function for video coding using affine global motion compensation.
We model the displacement estimation error during motion estimation and obtain the bit rate after applying the rate-distortion theory.
We assume that the displacement estimation error is caused by a perturbed affine transformation.
The 6 affine transformation parameters are assumed statistically independent, with each of them having a zero-mean Gaussian distributed estimation error.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about A FAST HEURISTIC FOR TILE PARTITIONING AND PROCESSOR ASSIGNMENT IN HEVC
- Log in to post comments
As the compression efficiency of HEVC comes at the cost of high complexity, especially in the encoder’s side, improved parallelization techniques that will speedup the encoding process are essential. One of the parallelization granules offered by HEVC is the tile level, whereby a frame is split into a grid like fashion with each resulting rectangular area (tile) being independently encoded. While tile parallelism has attracted research interest, the primary focus was to characterize performance and develop load balancing schemes assuming a one on one tile processor assignment.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
Dictionary learning is a popular method for obtaining sparse linear representations for high dimensional data, with many applications in image classification, signal processing and machine learning.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Regularized Gradient Descent Training of Steered Mixture of Experts for Sparse Image Representation
- Log in to post comments
The Steered Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) framework targets a sparse space-continuous representation for images, videos, and light fields enabling processing tasks such as approximation, denoising, and coding.
The underlying stochastic processes are represented by a Gaussian Mixture Model, traditionally trained by the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm.
We instead propose to use the MSE of the regressed imagery for a Gradient Descent optimization as primary training objective.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views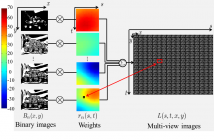
We propose an efficient coding scheme for a dense light field, i.e.,
a set of multi-viewpoint images taken with very small viewpoint intervals.
The key idea behind our proposal is that a light field is represented
only using weighted binary images, where several binary
images and corresponding weight values are to be chosen to optimally
approximate the light field. The coding scheme derived from
this idea is completely different from those of modern image/video
coding standards. However, we found that our scheme can achieve
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about A 4D DCT-BASED LENSLET LIGHT FIELD CODEC
- Log in to post comments
Light fields aim to represent visual information in 3D space. They are 4D structures that contain the images of a given scene from a sampled 2D range of viewpoints. When acquired using a lenslet camera, in addition to the ordinary intra-view redundancy, these views have a great deal of inter-view redundancy. In this work we propose a light field codec that fully exploits the 4D redundancy of light fields by using a 4D transform and hexadeca-trees. It initially divides the light field into 4D blocks and computes a 4D Discrete Cosine Transform of each one.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views