- Read more about SCALABLE LIGHT FIELD COMPRESSION SCHEME USING SPARSE RECONSTRUCTION AND RESTORATION
- Log in to post comments
This poster describes a light field scalable compression scheme based on the sparsity of the angular Fourier transform of the light field. A subset of sub-aperture images (or views) is compressed using HEVC as a base layer and transmitted to the decoder. An entire light field is reconstructed from this view subset using a method exploiting the sparsity of the light field in the continuous Fourier domain. The reconstructed light field is enhanced using a patch-based restoration method. Then, restored samples are used to predict original ones, in a SHVC-based SNR-scalable scheme.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Coding Sensitive based Approximation Algorithm for Power Efficient VBS-DCT VLSI Design in HEVC Hardwired Intra Encoder
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Coding Sensitive based Approximation Algorithm for Power Efficient VBS-DCT VLSI Design in HEVC Hardwired Intra Encoder
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 ViewsCurrent video coders rely heavily on block-based motion compensation, which is known to accurately capture pure translation, but to (at best) approximate all other types of motion, such as rotation and zoom. Moreover, as motion vectors are obtained through pixel-domain block matching to optimize a rate-distortion cost, and do not necessarily represent the actual motion, the model should not be considered a proper sampling of the underlying pixel motion field.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about AN EFFICIENT INTRA CODING ALGORITHM BASED ON STATISTICAL LEARNING FOR SCREEN CONTENT CODING
- Log in to post comments
Screen content has different characteristics compared with natural content captured by cameras. To achieve more efficient compression, some new coding tools have been developed in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Screen Content Coding (SCC) Extension, which also increase the computational complexity of encoder. In this paper, complexity analysis are first conducted to explore the distribution of complexities.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views- Read more about AN EFFICIENT INTRA CODING ALGORITHM BASED ON STATISTICAL LEARNING FOR SCREEN CONTENT CODING
- Log in to post comments
Screen content has different characteristics compared with natural content captured by cameras. To achieve more efficient compression, some new coding tools have been developed in the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) Screen Content Coding (SCC) Extension, which also increase the computational complexity of encoder. In this paper, complexity analysis are first conducted to explore the distribution of complexities.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about MULTIGAP: MULTI-POOLED INCEPTION NETWORK WITH TEXT AUGMENTATION FOR AESTHETIC PREDICTION OF PHOTOGRAPHS
- Log in to post comments
With the advent of deep learning, convolutional neural networks have solved many imaging problems to a large extent. However, it remains to be seen if the image “bottleneck” can be unplugged by harnessing complementary sources of data. In this paper, we present a new approach to image aesthetic evaluation that learns both visual and textual features simultaneously. Our network extracts visual features by appending global average pooling blocks on multiple inception modules (MultiGAP), while textual features from associated user comments are learned from a recurrent neural network.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views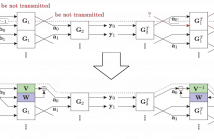
- Read more about PSUEDO REVERSIBLE SYMMETRIC EXTENSION FOR LIFTING-BASED NONLINEAR-PHASE PARAUNITARY FILTER BANKS
- Log in to post comments
This study presents a pseudo reversible symmetric extension (P-RevSE) that solves the signal boundary problem of lifting-based nonlinear-phase paraunitary filter banks (L-NLPPUFBs), which have high compression rates thanks to their not having a constraint on the linear-phase property unlike the existing transforms used in image coding standards. The conventional L-NLPPUFBs with a periodic extension (PE) yield annoying artifacts at the signal boundaries.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about Temporal Correlation based Hierarchical Quantization Parameter Determination for HEVC Video Coding
- Log in to post comments
The quantization parameter (QP) value and Lagrangian multiplier (λ) are the key factors for an encoder to achieve the trade-off between visual quality and bit-rate in next generation multimedia communications. In this work, we propose a novel temporal redundancy ratio (TRR) model to determinate hierarchical QPs.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views- Read more about Lifting‐based Illumination Adaptive Transform (LIAT) using Mesh‐based Illumination Modelling
- Log in to post comments
State-of-the-art video coding techniques employ block-based
illumination compensation to improve coding efficiency. In
this work, we propose a Lifting-based Illumination Adaptive
Transform (LIAT) to exploit temporal redundancy among
frames that have illumination variations, such as the frames
of low frame rate video or multi-view video. LIAT employs
a mesh-based spatially affine model to represent illumination
variations between two frames. In LIAT, transformed frames
are jointly compressed, together with illumination information,
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views