
- Read more about Video Compression with Arbitrary Rescaling Network
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Most video platforms provide video streaming services with different qualities, and the resolution of the videos usually adjusts the quality of the services. So high-resolution videos need to be downsampled for compression. In order to solve the problem of video coding at different resolutions, we propose a rate-guided arbitrary rescaling network (RARN) for video resizing before encoding.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Pixel-Wise Quantization for Image Compression
- Log in to post comments
Since the distortions on simple pixels are more noticeable than those on complex pixels, this paper proposes a pixel-wise quantization method, which allows to reduce the quantization parameters of simple pixels adaptively for the purpose of enhancing the subjective quality, and no additional syntax need to be transmitted in the bitstream. The discrimination of simple pixels is based on the texture complexity of the neighboring reconstruction pixels. The reduction of quantization parameters is related to the just noticeable difference for the human visual system.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Long-distance Information Filtering Network for Compressed Video Quality Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
Restoring high-quality videos from low-quality compressed ones is a crucial research topic in video coding. Most existing methods do not exploit the information in the long-distance compressed frames. Even when they do, these methods ignore the effect of interference information during reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a unique Long-distance Information Filtering (LIF) scheme with the 3D-CNN, which enhances compressed videos by mining filtered and valid information from long-distance frames.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
In the development of video coding standard, decoder-side motion derivation technology has been proven to provide promising coding efficiency. With this type of technology, the motion information is derived at the decoder instead of being signaled in the bitstream by the encoder, and thus, the number of bits to be sent are reduced. A typical decoder-side derivation technology is template matching, which refines the motion by finding the closest match between neighboring reconstructed samples and corresponding reference samples in the reference pictures.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views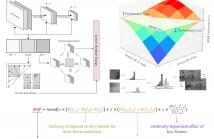
- Read more about An Adaptive Intra-frame Quantization Parameter Derivation Model Jointing with Inter-frame Analysis
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel quantization parameter (QP) derivation module that constructs several spatiotemporal characteristics into key-frame QP determination through an efficient pre-analysis progress. A series of simplified prediction modes and a histogram statistic are employed to model the reference quality that key-frames provide to subsequent frames. An adaptive delta-QP value is generated to address the conflict between the low compression efficiency of intra-only frames and the critical predictive basis of temporal-underlying frames.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views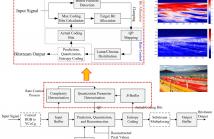
- Read more about An Efficient Rate Control Scheme for Video Compression in Low-latency Interoperable Interfaces
- Log in to post comments
Lightweight video compression has effectively alleviated the tension between growing transmission demands and expensive integration upgrades. Effective rate control algorithms are believed to be the crucial bottleneck for quality improvement during those ultra-high throughput coding processes. This paper proposes a novel rate control (RC) scheme that constructs a contextual adaptive bit estimation model through clustering historical compression information into block-gradient complexity categories.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
The new coding tools improved the performance for H.266/VVC but also brought challenges for hardware integer motion estimation (IME). First, the data dependency in deriving a predicted motion vector (PMV) is more severe. Second, the overhead of IME is increased by the complex partition mechanism. The challenges are tougher for IME in coding tree unit (CTU) level pipelined encoder. In this paper, we propose a hardware-friendly CTU-level IME algorithm with three innovative designs. First, a PMV prediction is proposed to derive PMVs in advance.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views
- Read more about Learning to Compress Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Captured Video: Benchmark and Analysis
- Log in to post comments
DCC-slides-clean.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Temporal Down-Sampling Based Video Coding with Frame-Recurrent Enhancement
- Log in to post comments
In many digital systems, the transmission bandwidth, as well as storage capacity, are usually very limited. This introduces challenges for both video transmission and video storage. One of the efficient solutions to this problem is to compress the down-sampled frames and then process up-sampling/super-resolution after decoding. To seek lower bit rates and further obtain high-quality up-sampled videos, this paper proposes a temporal down-sampling based
video coding system and a frame-recurrent enhancement based video upsampling strategy.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Zigzag Ordered Walsh Matrix for Compressed Sensing Image Sensor
- Log in to post comments
In compressed sensing (CS) based CMOS image sensors (CS-CIS), the ternary measurement matrix determines the compression performance in terms of decoded image quality versus sampling rate (data rate).In this paper, we propose a structured measurement matrix called Zigzag ordered Walsh matrix (ZoW). Firstly, the Walsh matrix is divided into several measurement patterns.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views