
- Read more about TEXTURE-BASED REGION TRACKING USING GAUSSIAN MARKOV RANDOM FIELDS FOR CILIA MOTION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
Region tracking becomes a challenging problem at the presence of low contrast and textured images such as cilia video images where beating cilia appear as moving texture. Tracking such patterns requires extracting of features that are capable of discriminating them effectively. In this paper, a method based on texture features for region tracking is proposed. The texture features are extracted from a sequence of images using Gaussian Markov Random Fields (GMRF). These features are employed to track the motion of a given region and extract its trajectory.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Fast Adaptive Bilateral Filtering of Color Images
- Log in to post comments
The bilateral filter is popularly used for image enhancement. By using a range kernel along with a spatial kernel, the filter is able to smooth images without excessive blurring of edges. It has been shown that the enhancement capacity of the filter can be boosted by adapting the width of the range kernel at each pixel. A fast algorithm for grayscale images was recently proposed for this so-called adaptive bilateral filter, which is otherwise computationally expensive. This can trivially be extended for color filtering using channelwise processing.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGE FUSION USING FAST HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DENOISING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about FAST HIGH-DIMENSIONAL BILATERAL AND NONLOCAL MEANS FILTERING
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about FAST HIGH-DIMENSIONAL BILATERAL AND NONLOCAL MEANS FILTERING
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views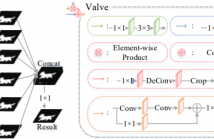
- Read more about Revisiting Multi-level Feature Fusion: A Simple yet Effective Network for Salient Object Detection
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Fashion style recognition using component-dependent convolutional neural networks
- Log in to post comments
The fashion style recognition is important in online marketing applications. Several algorithms have been proposed, but their accuracy is still unsatisfactory. In this paper, we share our proposed method for creating an improved fashion style recognition algorithm, component-dependent convolutional neural networks (CD-CNNs). Given that a lot of fashion styles largely depend on the features of specific body parts or human body postures, first, we obtain images of the body parts and postures by using semantic segmentation and pose estimation algorithms; then, we pre-train CD-CNNs.
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views
- Read more about MULTIPLE INSTANCE DENSE CONNECTED CONVOLUTION NEURAL NETWORK FOR AERIAL IMAGE SCENE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
With the development of deep learning, many state-of-the-art natural image scene classification methods have demonstrated impressive performance. While the current convolution neural network tends to extract global features and global semantic information in a scene, the geo-spatial objects can be located at anywhere in an aerial image scene and their spatial arrangement tends to be more complicated. One possible solution is to preserve more local semantic information and enhance feature propagation.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Virtual Reality Video Quality Assessment Based on 3D Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
As a new medium, Virtual Reality (VR) has attracted widespread attentions and research interests. More and more researchers have built their VR image/video database and devise related algorithms. However, the existing methods of VR video quality assessment are not very effective, and one of the most important reasons is that the database is not suitable. To this end, this paper proposes an efficient VR quality assessment method on self-built database.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about SF-CNN: A Fast Compression Artifacts Removal via Spatial-to-Frequency Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose SF-CNN, a fast convolutional neural network structure for JPEG image compression artifacts removal. Recently, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based image restoration has shown great performance improvement. However, their heavy computational cost makes it difficult to apply other applications such as high-level vision tasks. Since heavy computation arises from maintaining spatial resolution of an input image, some works make a structure which is composed of spatial downsampling and
- Categories:
 88 Views
88 Views