
Product placement, also called advertisement embedding, is to place some specific products in an image or a video, which may attract consumers to buy their products. However, adding advertisement objects in images is difficult, because where to add the product and how to fuse the background must be concerned. In this paper, to overcome this issue, we present a novel hierarchical framework with conditional generative adversarial network to add advertisement object in all kinds of scene images. The key point of our framework is leaning the relation between surrounding and products .
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about AUTODEPTH: SINGLE IMAGE DEPTH MAP ESTIMATION VIA RESIDUAL CNN ENCODER-DECODER AND STACKED HOURGLASS
- Log in to post comments
We address the task of estimating depth from a single intensity image via a novel convolutional neural network (CNN) encoder-decoder architecture, which learns the depth information using example pairs of color images and their corresponding depth maps. The proposed model integrates residual connections within pooling and up-sampling layers, and hourglass networks which operate on the encoded features, thus processing these at various scales. Furthermore, the model is optimized under the constraints of perceptual as well as the mean squared error loss.
eposter_autodepth.pdf
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views
- Read more about CONTINUOUS HAND GESTURE SPOTTING AND CLASSIFICATION USING 3D FINGER JOINTS INFORMATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a novel approach for continuous dynamic hand gesture recognition for RGB video input. Our approach contains two main modules. Firstly, in the gesture spotting module, the video sequence with continuous gestures are pre-segmented into isolated gestures. Secondly, the gesture classification module classifies the segmented gestures. In the gesture spotting module, the motion of the hand palm and finger movements are fed into Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) network for gesture spotting purpose.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Read more about PEDESTRIAN ATTRIBUTE RECOGNITION BASED ON MTCNN WITH ONLINE BATCH WEIGHTED LOSS
- Log in to post comments
Due to the large number and huge diversity of attributes, pedestrian attribute recognition in video surveillance scenarios is a challenging task in the field of computer vision. Different from most previous works which only focus on extremely imbalanced attribute distribution problem, a new grouping way of attributes based multi-task convolutional neural network (MTCNN) is put forward, which exploits the spatial correlations among attributes and guarantees some independence of each attribute as well.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about A 3D FACE MODELING APPROACH FOR IN-THE-WILD FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION ON IMAGE DATASETS
- Log in to post comments
This paper explores the benefits of 3D face modeling for in-the-wild facial expression recognition (FER). Since there is limited in-the-wild 3D FER dataset, we first construct 3D facial data from available 2D dataset using recent advances in 3D face reconstruction. The 3D facial geometry representation is then extracted by deep learning technique. In addition, we also take advantage of manipulating the 3D face, such as using 2D projected images of 3D face as additional input for FER. These features are then fused with that of 2D FER typical network.
- Categories:
 82 Views
82 Views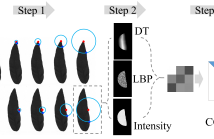
This paper presents a novel shape descriptor to effectively and efficiently characterize the local image statistics. The proposed descriptor, termed contour covariance (CC), characterizes covariance features driven by a moving point on the shape contour at multiple scales. To calculate the covariance matrices, three basic features including texture, intensity and distance map, are extracted from the object image. Based on coefficients of the obtained covariance matrices, the proposed CC descriptor is compact yet informative, as well as invariant to rotation, translation and scale.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views- Read more about Poster of SDSEN: Self-Refining Deep Symmetry Enhanced Network for Rain Removal
- Log in to post comments
Rain removal aims to remove the rain streaks on rain images. The state-of-the-art methods are mostly based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). However, as CNN is not equivariant to object rotation, these methods are unsuitable for dealing with the tilted rain streaks. To tackle this problem, we propose Deep Symmetry Enhanced Network (DSEN) that is able to explicitly extract the rotation equivariant features from rain images. In addition, we design a self-refining mechanism to remove the accumulated rain streaks in a coarse-to-fine manner.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about FAST: Flow-Assisted Shearlet Transform for Densely-sampled Light Field Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
Shearlet Transform (ST) is one of the most effective methods for Densely-Sampled Light Field (DSLF) reconstruction from a Sparsely-Sampled Light Field (SSLF). However, ST requires a precise disparity estimation of the SSLF. To this end, in this paper a state-of-the-art optical flow method, i.e. PWC-Net, is employed to estimate bidirectional disparity maps between neighboring views in the SSLF. Moreover, to take full advantage of optical flow and ST for DSLF reconstruction, a novel learning-based method, referred to as Flow-Assisted Shearlet Transform (FAST), is proposed in this paper.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about PERSON-SPECIFIC JOY EXPRESSION SYNTHESIS WITH GEOMETRIC METHOD
- Log in to post comments
Smiling has a psychiatric effect in emotional state and may hold tremendous potential for clinical remediation in psychiatric disorders. A few researchers in image synthesis work on acting on the emotional state of subjects by automatically deforming their faces to synthesize joyful expression. However, to generate these expressions they apply the same deformation for the subjects while each person smiles differently. In this paper, we head towards a personalized synthesis of the joy expression.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
Visual tracking is a very important and challenging problem in the field of computer vision. In recent years, Siamese networks have been widely used for visual tracking due to their fast tracking speed, but many trackers based on Siamese network train their networks by utilizing either pairwise loss or triplet loss, which easily leads to over-fitting. In addition, it is difficult to distinguish some hard samples in the training samples. In this paper, we propose a novel global similarity loss to train the network.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views