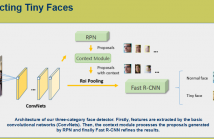
- Read more about A THREE-CATEGORY FACE DETECTOR WITH CONTEXTUAL INFORMATION ON FINDING TINY FACES
- Log in to post comments
Great progresses have been achieved on object detection in the wild. However, it still remains a challenging problem due to tiny objects. In this paper, we present a Three-category Classification Neural Network to find tiny faces under complex environments by leveraging contextual information around faces. Tiny faces (within 20x20 pixels) are so fuzzy that the facial patterns are not clear or even ambiguous for detection.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about A NOVEL CONFIDENCE MEASURE FOR DISPARITY MAPS BY PIXEL-WISE COST FUNCTION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A-CCNN: Adaptive CCNN for Density Estimation and Crowd Counting
- Log in to post comments
Crowd counting, for estimating the number of people in a crowd using vision-based computer techniques, has attracted much interest in the research community. Although many attempts have been reported, real-world problems, such as huge variation in subjects’ sizes in images and serious occlusion among people, make it still a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose an Adaptive Counting Convolutional Neural Network (A-CCNN) and consider the scale variation of objects in a frame adaptively so as to improve the accuracy of counting.
ICIP2018.pptx
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views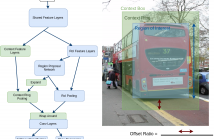
- Read more about IMPROVING PROPOSAL-BASED OBJECT DETECTION USING CONVOLUTIONAL CONTEXT FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
A novel extension to proposal-based detection is proposed in order to learn convolutional context features for determining boundaries of objects better. Objects and their context are aimed to be learned through parallel convolutional stages. The resulting object and context feature maps are combined in such a way that they preserve their spatial relationship. The proposed algorithm is trained and evaluated on PASCAL VOC 2007 detection benchmark dataset and yielded improvements in performance over baseline, for all classes, especially the ones with distinctive context.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about INDOOR DENSE DEPTH MAP AT DRONE HOVERING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about An Online Algorithm for Constrained Face Clustering in Videos
- Log in to post comments
This is the poster for the ICIP 2018 paper titled "An Online Algorithm for Constrained Face Clustering in Videos".
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about THE COUPLED TUFF-BFF ALGORITHM FOR AUTOMATIC 3D SEGMENTATION OF MICROGLIA
- Log in to post comments
We propose an automatic 3D segmentation algorithm for multiphoton microscopy images of microglia. Our method is capable of segmenting tubular and blob-like structures from noisy images. Current segmentation techniques and software fail to capture the fine processes and soma of the microglia cells, useful for the study of the microglia role in the brain during healthy and diseased states. Our coupled tubularity flow field (TuFF)-blob flow field (BFF) method evolves a level set towards the object boundary using the directional tubularity and blobness measure of 3D images.
icip18.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about SEQUENTIAL RECOGNITION OF MANIPULATION ACTIONS USING DISCRIMINATIVE SUPERPIXEL GROUP MINING
- Log in to post comments
Activities such as those involved in food preparation involve interactions between hands, tools and multiple manipulated objects that affect them in visually complex ways making recognition of their constituent actions challenging. We describe a system that classifies action classes in such a setting based on discriminative spatio-temporal superpixel groups. The entire system operates sequentially enabling online action recognition. We obtain state-of-the-art results whilst employing a compact, interpretable representation.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about SUPERRESOLUTION CONTOUR RECONSTRUCTION APPROACH TO A LINEAR THERMAL EXPANSION MEASUREMENT
- Log in to post comments
Optical imaging delivers absolute, non-contact, and high-dynamic-range measurement of thermal expansion. However, to achieve high accuracy, various factors should be accounted within the image analysis, including: image spatial sampling, lens aberrations, brightness nonuniformity and object edge deformations. Approach based on the object contour reconstruction is presented. Measurement procedure consists of two stages. Firstly, object edge contours corresponding to different temperatures are estimated.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views